forked from bevyengine/bevy
-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 1
New issue
Have a question about this project? Sign up for a free GitHub account to open an issue and contact its maintainers and the community.
By clicking “Sign up for GitHub”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy statement. We’ll occasionally send you account related emails.
Already on GitHub? Sign in to your account
Draw error #6
Merged
Merged
Draw error #6
Conversation
This file contains bidirectional Unicode text that may be interpreted or compiled differently than what appears below. To review, open the file in an editor that reveals hidden Unicode characters.
Learn more about bidirectional Unicode characters
…evyengine#13763) # Objective Fixes bevyengine#13711 ## Solution Introduce smaller, generic system sets for each schedule variant, which are ordered against other generic variants: - `ExitSchedules<S>` - For `OnExit` schedules, runs from leaf states to root states. - `TransitionSchedules<S>` - For `OnTransition` schedules, runs in arbitrary order. - `EnterSchedules<S>` - For `OnEnter` schedules, runs from root states to leaf states. Also unified `ApplyStateTransition<S>` schedule which works in basically the same way, just for internals. ## Testing - One test that tests schedule execution order --------- Co-authored-by: Lee-Orr <[email protected]>
# Objective The error printed-out due to a missing shader file was confusing; This PR changes the error message. Fixes bevyengine#13644 ## Solution I replaced the confusing wording (`... shader is not loaded yet`) with a clear explanation (`... shader could not be loaded`) ## Testing > Did you test these changes? If so, how? removing `assets/shaders/game_of_life.wgsl` & running its associated example now produces the following error: ``` thread '<unnamed>' panicked at examples/shader/compute_shader_game_of_life.rs:233:25: Initializing assets/shaders/game_of_life.wgsl: Pipeline could not be compiled because the following shader could not be loaded: AssetId<bevy_render::render_resource::shader::Shader>{ index: 0, generation: 0} note: run with `RUST_BACKTRACE=1` environment variable to display a backtrace Encountered a panic in system `bevy_render::renderer::render_system`! ``` I don't think there are any tests expecting the previous error message, so this change should not break anything. > Are there any parts that need more testing? If there was an intent behind the original message, this might need more attention. > How can other people (reviewers) test your changes? Is there anything specific they need to know? One should be able to preview the changes by running any example after deleting/renaming their associated shader(s). > If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are there any important ones you can't test? N/A
bevyengine#13772) The documentation for the `State` resource still referenced the use of `apply_state_transition` to manually force a state transition to occur, and the question around how to force transitions had come up a few times on discord. This is a docs-only change, that does the following: - Properly references `StateTransition` in the `MainSchedule` docs - replace the explanations for applying `NextState` with ones that explain the `StateTransition` schedule, and mentions the possibility of calling it manually - Add an example of calling `StateTransition` manually in the docs for the state transition schedule itself. --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <[email protected]>
) # Objective - If the fog is disabled it still generates a useless branch which can hurt performance ## Solution - Make the flag a shader_def instead ## Testing - I tested enabling/disabling fog works as expected per-material in the fog example - I also tested that scenes that don't add the FogSettings resource still work correctly ## Review notes I'm not sure how to handle the removed material flag. Right now I just commented it out and added a not to reuse it instead of creating a new one.
# Objective - My attempt at fulfilling bevyengine#13629. ## Solution Renames the `and_then` / `or_else` run condition methods to `and` / `or`, respectively. Extends the run conditions API to include a suite of binary logical operators: - `and` - `or` - `nand` - `nor` - `xor` - `xnor` ## Testing - Did you test these changes? If so, how? - The test **run_condition_combinators** was extended to include the added run condition combinators. A **double_counter** system was added to test for combinators running on even count cycles. - Are there any parts that need more testing? - I'm not too sure how I feel about the "counter" style of testing but I wanted to keep it consistent. If it's just a unit test I would prefer simply to just assert `true` == _combinator output_ or `false` == _combinator output_ . - How can other people (reviewers) test your changes? Is there anything specific they need to know? - Nothing too specific. The added methods should be equivalent to the logical operators they are analogous to (`&&` , `||`, `^`, `!`). - If relevant, what platforms did you test these changes on, and are there any important ones you can't test? - Should not be relevant, I'm using Windows. ## Changelog - What changed as a result of this PR? - The run conditions API. - If applicable, organize changes under "Added", "Changed", or "Fixed" sub-headings - Changed: - `and_then` run condition combinator renamed to simply `and` - `or_else` run condition combinator renamed to simply `or` - Added: - `nand` run condition combinator. - `nor` run condition combinator. - `xor` run condition combinator. - `xnor` run condition combinator. ## Migration Guide - The `and_then` run condition method has been replaced with the `and` run condition method. - The `or_else` run condition method has been replaced with the `or` run condition method. --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <[email protected]> Co-authored-by: Andres O. Vela <[email protected]>
# Objective There were some issues with the `serialize` feature: - `bevy_app` had a `serialize` feature and a dependency on `serde` even there is no usage of serde at all inside `bevy_app` - the `bevy_app/serialize` feature enabled `bevy_ecs/serde`, which is strange - `bevy_internal/serialize` did not enable `bevy_app/serialize` so there was no way of serializing an Entity in bevy 0.14 ## Solution - Remove `serde` and `bevy_app/serialize` - Add a `serialize` flag on `bevy_ecs` that enables `serde` - ` bevy_internal/serialize` now enables `bevy_ecs/serialize`
…vyengine#13788) i based the design on @mgi388 in the discussion about the issue. i added the illustration in such a way that it shows up when you hover your mouse over the type, i hope this is what was meant by the issue no unit tests were added bc obviously Fixes bevyengine#13664
Fixes bevyengine#13758. # Objective Calling `update` on the main app already calls `clear_trackers`. Calling it again in `SubApps::update` caused RemovedCompenet Events to be cleared earlier than they should be. ## Solution - Don't call clear_trackers an extra time. ## Testing I manually tested the fix with this unit test: ``` #[cfg(test)] mod test { use crate::core::{FrameCount, FrameCountPlugin}; use crate::prelude::*; #[test] fn test_next_frame_removal() { #[derive(Component)] struct Foo; #[derive(Resource)] struct RemovedCount(usize); let mut app = App::new(); app.add_plugins(FrameCountPlugin); app.add_systems(Startup, |mut commands: Commands| { for _ in 0..100 { commands.spawn(Foo); } commands.insert_resource(RemovedCount(0)); }); app.add_systems(First, |counter: Res<FrameCount>| { println!("Frame {}:", counter.0) }); fn detector_system( mut removals: RemovedComponents<Foo>, foos: Query<Entity, With<Foo>>, mut removed_c: ResMut<RemovedCount>, ) { for e in removals.read() { println!(" Detected removed Foo component for {e:?}"); removed_c.0 += 1; } let c = foos.iter().count(); println!(" Total Foos: {}", c); assert_eq!(c + removed_c.0, 100); } fn deleter_system(foos: Query<Entity, With<Foo>>, mut commands: Commands) { foos.iter().next().map(|e| { commands.entity(e).remove::<Foo>(); }); } app.add_systems(Update, (detector_system, deleter_system).chain()); app.update(); app.update(); app.update(); app.update(); } } ```
# Objective Reading system information severely slows down the update loop. Fixes bevyengine#12848. ## Solution Read system info in a separate thread. ## Testing - Open the scene 3d example - Add `FrameTimeDiagnosticsPlugin`, `SystemInformationDiagnosticsPlugin` and `LogDiagnosticsPlugin` to the app. - Add this system to the update schedule to disable Vsync on the main window ```rust fn change_window_mode(mut windows: Query<&mut Window, Added<Window>>) { for mut window in &mut windows { window.present_mode = PresentMode::AutoNoVsync; } } ``` - Read the fps values in the console before and after this PR. On my PC I went from around 50 fps to around 1150 fps. --- ## Changelog ### Changed - The `SystemInformationDiagnosticsPlugin` now reads system data separate of the update cycle. ### Added - The `EXPECTED_SYSTEM_INFORMATION_INTERVAL` constant which defines how often we read system diagnostic data. --------- Co-authored-by: IceSentry <[email protected]>
# Objective - Mikktspace requires that we normalize world normals/tangents _before_ interpolation across vertices, and then do _not_ normalize after. I had it backwards. - We do not (am not supposed to?) need a second set of barycentrics for motion vectors. If you think about the typical raster pipeline, in the vertex shader we calculate previous_world_position, and then it gets interpolated using the current triangle's barycentrics. ## Solution - Fix normal/tangent processing - Reuse barycentrics for motion vector calculations - Not implementing this for 0.14, but long term I aim to remove explicit vertex tangents and calculate them in the shader on the fly. ## Testing - I tested out some of the normal maps we have in repo. Didn't seem to make a difference, but mikktspace is all about correctness across various baking tools. I probably just didn't have any of the ones that would cause it to break. - Didn't test motion vectors as there's a known bug with the depth buffer and meshlets that I'm waiting on the render graph rewrite to fix.
…to_world_with (bevyengine#13800) # Objective - bevyengine#13714 broke scenes pretty seriously - Fixes bevyengine#13796 ## Solution Revert it. We can redo this PR once the behavior is fixed. Co-authored-by: Dmytro Banin <[email protected]>
# Objective - Add a new example showcasing how to add custom primitives and what you can do with them. ## Solution - Added a new example `custom_primitives` with a 2D heart shape primitive highlighting - `Bounded2d` by implementing and visualising bounding shapes, - `Measured2d` by implementing it, - `Meshable` to show the shape on the screen - The example also includes an `Extrusion<Heart>` implementing - `Measured3d`, - `Bounded3d` using the `BoundedExtrusion` trait and - meshing using the `Extrudable` trait. ## Additional information Here are two images of the heart and its extrusion:   --------- Co-authored-by: Jakub Marcowski <[email protected]>
…e#13791) # Objective Closes bevyengine#13738 ## Solution Added `from_color` to materials that would support it. Didn't add `from_color` to `WireframeMaterial` as it doesn't seem we expect users to be constructing them themselves. ## Testing None --- ## Changelog ### Added - `from_color` to `StandardMaterial` so you can construct this material from any color type. - `from_color` to `ColorMaterial` so you can construct this material from any color type.
# Objective - Split the bevy_ecs::events module so it's easier to work with ## Solution - Split the event.rs file across multiple files, made sure all tests passed, and exports from the module were the same as previous ## Testing - All automated tests pass.
…ngine#13783)" (bevyengine#13803) This reverts commit 3ced49f. Relevant to bevyengine#13802. This wasn't done quite right and partially broke fog. Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <[email protected]>
bevyengine#13804) …izer (bevyengine#13442)" This reverts commit 5cfb063. - This PR broke bevy-trait-query, which needs to be able to write a resource in init_state. See bevyengine#13798 for more details. - Note this doesn't fix everything as transmutes for bevy-trait-query will still be broken,. But the current usage in that crate is UB, so we need to find another solution.
# Objective - Correct typos in docs for `Query::join`'s docs ## Solution - Fix them Co-authored-by: François Mockers <[email protected]>
The examples won't work when copy-pasted to another project, without also copying their shader files. This change adds constants at the top of the files to bring attention to the dependencies. Follow up to [bevyengine#13624](bevyengine#13624 (comment))
…evyengine#13808) # Objective As discovered in Leafwing-Studios/leafwing-input-manager#538, there appears to be some real weirdness going on in how event updates are processed between Bevy 0.13 and Bevy 0.14. To identify the cause and prevent regression, I've added tests to validate the intended behavior. My initial suspicion was that this would be fixed by bevyengine#13762, but that doesn't seem to be the case. Instead, events appear to never be updated at all when using `bevy_app` by itself. This is part of the problem resolved by bevyengine#11528, and introduced by bevyengine#10077. After some investigation, it appears that `signal_event_update_system` is never added using a bare-bones `App`, and so event updates are always skipped. This can be worked around by adding your own copy to a later-in-the-frame schedule, but that's not a very good fix. ## Solution Ensure that if we're not using a `FixedUpdate` schedule, events are always updated every frame. To do this, I've modified the logic of `event_update_condition` and `event_update_system` to clearly and correctly differentiate between the two cases: where we're waiting for a "you should update now" signal and where we simply don't care. To encode this, I've added the `ShouldUpdateEvents` enum, replacing a simple `bool` in `EventRegistry`'s `needs_update` field. Now, both tests pass as expected, without having to manually add a system! ## Testing I've written two parallel unit tests to cover the intended behavior: 1. Test that `iter_current_update_events` works as expected in `bevy_ecs`. 2. Test that `iter_current_update_events` works as expected in `bevy_app` I've also added a test to verify that event updating works correctly in the presence of a fixed main schedule, and a second test to verify that fixed updating works at all to help future authors narrow down failures. ## Outstanding - [x] figure out why the `bevy_app` version of this test fails but the `bevy_ecs` version does not - [x] figure out why `EventRegistry::run_updates` isn't working properly - [x] figure out why `EventRegistry::run_updates` is never getting called - [x] figure out why `event_update_condition` is always returning false - [x] figure out why `EventRegistry::needs_update` is always false - [x] verify that the problem is a missing `signal_events_update_system` --------- Co-authored-by: Mike <[email protected]>
# Objective - temporary fix for CI - Rust 1.79 seems to have broken bevy on DX12 on some configuration ## Solution - Keep using Rust 1.78
StatesPlugin and GizmoPlugin were missing from the doc comment of DefaultPlugins. I am not sure whether this was for a reason, but i just stumbled over it and it seemed off... ## Testing I'm not sure how to test these changes?
# Objective While learning about shaders and pipelines, I found this example to be misleading; it wasn't clear to me how the node knew what the correct "instance" of `PostProcessSettings` we should send to the shader (as the combination of `ExtractComponentPlugin` and `UniformComponentPlugin` extracts + sends _all_ of our `PostProcessSetting` components to the GPU). The goal of this PR is to clarify how to target the view specific `PostProcessSettings` in the shader when there are multiple cameras. ## Solution To accomplish this, we can use a dynamic uniform buffer for `PostProcessSettings`, querying for the relevant `DynamicUniformIndex` in the `PostProcessNode` to get the relevant index to use with the bind group. While the example in its current state is _correct_, I believe that fact that it's intended to showcase a per camera post processing effect warrants a dynamic uniform buffer (even though in the context of this example we have only one camera, and therefore no adverse behaviour). ## Testing - Run the `post_processing` example before and after this change, verifying they behave the same. ## Reviewer notes This is my first PR to Bevy, and I'm by no means an expert in the world of rendering (though I'm trying to learn all I can). If there's a better way to do this / a reason not to take this route, I'd love to hear it! Thanks in advance.
# Objective - Fixes bevyengine#13807 ## Solution - Before this pr we antialiased between 0.5 and -0.5. This pr changes things to antialias between 0.25 and -0.25. I tried slightly larger ranges, but the edge between the boxes still showed. I'm not 100% sure this is the correct solution, but from what I could find the range you use is more art than science. ## Testing - Ran rounded_borders example, the code in the linked issue, and the testing example from bevyengine#12702. --- ## Changelog - reduce antialiasing in ui shader.
Currently blocked on gfx-rs/wgpu#5774 # Objective Update to wgpu 0.20 ## Solution Update to wgpu 0.20 and naga_oil 0.14. ## Testing Tested a few different examples on linux (vulkan, webgl2, webgpu) and windows (dx12 + vulkan) and they worked. --- ## Changelog - Updated to wgpu 0.20. Note that we don't currently support wgpu's new pipeline overridable constants, as they don't work on web currently and need some more changes to naga_oil (and are somewhat redundant with naga_oil's shader defs). See wgpu's changelog for more https://github.com/gfx-rs/wgpu/blob/trunk/CHANGELOG.md#v0200-2024-04-28 ## Migration Guide TODO --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <[email protected]> Co-authored-by: François Mockers <[email protected]>
…vyengine#13849) # Objective - bevyengine/bevy-website#1404 updates `code-validation` on the website to use the latest release candidate. - It also adds instructions to update this version for each new release candidate. - @alice-i-cecile asked [that this is added to the release checklist](bevyengine/bevy-website#1404 (comment)). ## Solution - Add a note to the post-release section for release candidates. ## Testing - No testing needed :)
# Objective when a parent container is auto-sized, text alignments `Center` and `Right` don't align to the center and right properly. fix it ## Solution ab_glyph positions return +/- values from an anchor point. we currently transform them to positive values from the min-x of the glyphs, and then offset from the left of the bounds. instead, we can keep the negative values as ab_glyph intended and offset from the left/middle/right of the bounds as appropriate. ## Testing texts with align left, center, right, all contained in the purple boxes: before (0.14.0-rc.2):  after:  code: ```rs use bevy::prelude::*; fn main() { App::new() .add_plugins(DefaultPlugins) .add_systems(Startup, setup) .run(); } fn setup(mut commands: Commands) { commands.spawn(Camera2dBundle::default()); for (left, justify) in [ (100.0, JustifyText::Left), (500.0, JustifyText::Center), (900.0, JustifyText::Right), ] { commands // container .spawn(NodeBundle { style: Style { flex_direction: FlexDirection::Column, position_type: PositionType::Absolute, left: Val::Px(left), top: Val::Px(100.0), width: Val::Px(300.0), ..Default::default() }, ..Default::default() }) .with_children(|commands| { commands.spawn(NodeBundle{ style: Style { flex_direction: FlexDirection::Row, height: Val::Px(75.0), ..Default::default() }, background_color: Color::srgb(1.0, 0.0, 1.0).into(), ..Default::default() }).with_children(|commands| { // a div that reduces the available size commands.spawn(NodeBundle { style: Style { width: Val::Px(75.0), ..Default::default() }, background_color: Color::srgb(0.0, 1.0, 0.0).into(), ..Default::default() }); // text with width=auto, but actual size will not be what it expcets due to the sibling div above commands.spawn(TextBundle { text: Text::from_section("Some text that wraps onto a second line", Default::default()).with_justify(justify), style: Style { align_self: AlignSelf::Center, ..Default::default() }, ..Default::default() }); }); }); } } ```
# Objective Fixes bevyengine#13815 ## Solution Move insertion of the plugin name to after build is called. ## Testing I added a regression test --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <[email protected]> Co-authored-by: François Mockers <[email protected]> Co-authored-by: François Mockers <[email protected]>
# Objective - Fixes bevyengine#13844 - Warn user when initializing state multiple times ## Solution - `insert_state` will overwrite previously initialized state value, reset transition events and re-insert it's own transition event. - `init_state`, `add_sub_state`, `add_computed_state` are idempotent, so calling them multiple times will emit a warning. ## Testing - 2 tests confirming overwrite works. - Given the example from bevyengine#13844 ```rs use bevy::prelude::*; fn main() { App::new() .add_plugins(DefaultPlugins) .insert_state(AppState::A) .insert_state(AppState::B) .add_systems(OnEnter(AppState::A), setup_a) .add_systems(OnEnter(AppState::B), setup_b) .add_systems(OnExit(AppState::A), cleanup_a) .add_systems(OnExit(AppState::B), cleanup_b) .run(); } #[derive(States, Debug, Clone, PartialEq, Eq, Hash)] enum AppState { A, B, } fn setup_a() { info!("setting up A"); } fn setup_b() { info!("setting up B"); } fn cleanup_a() { info!("cleaning up A"); } fn cleanup_b() { info!("cleaning up B"); } ``` We get the following result: ``` INFO states: setting up B ``` which matches our expectations.
# Objective
- Provide an expressive way to register dynamic behavior in response to
ECS changes that is consistent with existing bevy types and traits as to
provide a smooth user experience.
- Provide a mechanism for immediate changes in response to events during
command application in order to facilitate improved query caching on the
path to relations.
## Solution
- A new fundamental ECS construct, the `Observer`; inspired by flec's
observers but adapted to better fit bevy's access patterns and rust's
type system.
---
## Examples
There are 3 main ways to register observers. The first is a "component
observer" that looks like this:
```rust
world.observe(|trigger: Trigger<OnAdd, Transform>, query: Query<&Transform>| {
let transform = query.get(trigger.entity()).unwrap();
});
```
The above code will spawn a new entity representing the observer that
will run it's callback whenever the `Transform` component is added to an
entity. This is a system-like function that supports dependency
injection for all the standard bevy types: `Query`, `Res`, `Commands`
etc. It also has a `Trigger` parameter that provides information about
the trigger such as the target entity, and the event being triggered.
Importantly these systems run during command application which is key
for their future use to keep ECS internals up to date. There are similar
events for `OnInsert` and `OnRemove`, and this will be expanded with
things such as `ArchetypeCreated`, `TableEmpty` etc. in follow up PRs.
Another way to register an observer is an "entity observer" that looks
like this:
```rust
world.entity_mut(entity).observe(|trigger: Trigger<Resize>| {
// ...
});
```
Entity observers run whenever an event of their type is triggered
targeting that specific entity. This type of observer will de-spawn
itself if the entity (or entities) it is observing is ever de-spawned so
as to not leave dangling observers.
Entity observers can also be spawned from deferred contexts such as
other observers, systems, or hooks using commands:
```rust
commands.entity(entity).observe(|trigger: Trigger<Resize>| {
// ...
});
```
Observers are not limited to in built event types, they can be used with
any type that implements `Event` (which has been extended to implement
Component). This means events can also carry data:
```rust
#[derive(Event)]
struct Resize { x: u32, y: u32 }
commands.entity(entity).observe(|trigger: Trigger<Resize>, query: Query<&mut Size>| {
let event = trigger.event();
// ...
});
// Will trigger the observer when commands are applied.
commands.trigger_targets(Resize { x: 10, y: 10 }, entity);
```
You can also trigger events that target more than one entity at a time:
```rust
commands.trigger_targets(Resize { x: 10, y: 10 }, [e1, e2]);
```
Additionally, Observers don't _need_ entity targets:
```rust
app.observe(|trigger: Trigger<Quit>| {
})
commands.trigger(Quit);
```
In these cases, `trigger.entity()` will be a placeholder.
Observers are actually just normal entities with an `ObserverState` and
`Observer` component! The `observe()` functions above are just shorthand
for:
```rust
world.spawn(Observer::new(|trigger: Trigger<Resize>| {});
```
This will spawn the `Observer` system and use an `on_add` hook to add
the `ObserverState` component.
Dynamic components and trigger types are also fully supported allowing
for runtime defined trigger types.
## Possible Follow-ups
1. Deprecate `RemovedComponents`, observers should fulfill all use cases
while being more flexible and performant.
2. Queries as entities: Swap queries to entities and begin using
observers listening to archetype creation triggers to keep their caches
in sync, this allows unification of `ObserverState` and `QueryState` as
well as unlocking several API improvements for `Query` and the
management of `QueryState`.
3. Trigger bubbling: For some UI use cases in particular users are
likely to want some form of bubbling for entity observers, this is
trivial to implement naively but ideally this includes an acceleration
structure to cache hierarchy traversals.
4. All kinds of other in-built trigger types.
5. Optimization; in order to not bloat the complexity of the PR I have
kept the implementation straightforward, there are several areas where
performance can be improved. The focus for this PR is to get the
behavior implemented and not incur a performance cost for users who
don't use observers.
I am leaving each of these to follow up PR's in order to keep each of
them reviewable as this already includes significant changes.
---------
Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <[email protected]>
Co-authored-by: MiniaczQ <[email protected]>
Co-authored-by: Carter Anderson <[email protected]>
# Objective This is the first of a series of PRs intended to begin the upstreaming process for `bevy_mod_picking`. The purpose of this PR is to: + Create the new `bevy_picking` crate + Upstream `CorePlugin` as `PickingPlugin` + Upstream the core pointer and backend abstractions. This code has been ported verbatim from the corresponding files in [bevy_picking_core](https://github.com/aevyrie/bevy_mod_picking/tree/main/crates/bevy_picking_core/src) with a few tiny naming and docs tweaks. The work here is only an initial foothold to get the up-streaming process started in earnest. We can do refactoring and improvements once this is in-tree. --------- Co-authored-by: Aevyrie <[email protected]> Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <[email protected]>
# Objective - Actually use the value assigned to `d_xz`, like in [the original SMAA implementation](https://github.com/iryoku/smaa/blob/master/SMAA.hlsl#L960). This not already being the case was likely a mistake when converting from HLSL to WGSL ## Solution - Use `d_xz.x` and `d_xz.y` instead of `d.x` and `d.z` ## Testing - Quickly tested on Windows 11, `x86_64-pc-windows-gnu` `1.79.0` with the latest NVIDIA drivers. App runs with SMAA enabled and everything seems to work as intended - I didn't observe any major visual difference between this and the previous version, though this should be more correct as it matches the original SMAA implementation
# Objective - Adopted from bevyengine#11460. - Closes bevyengine#7332. - The documentation for `DefaultPlugins` and `MinimalPlugins` frequently goes out of date because it is not . ## Solution - Create a macro, `plugin_group!`, to automatically create `PluginGroup`s and document them. ## Testing - Run `cargo-expand` on the generated code for `DefaultPlugins` and `MinimalPlugins`. - Try creating a custom plugin group with the macro. --- ## Showcase - You can now define custom `PluginGroup`s using the `plugin_group!` macro. ```rust plugin_group! { /// My really cool plugic group! pub struct MyPluginGroup { physics:::PhysicsPlugin, rendering:::RenderingPlugin, ui:::UiPlugin, } } ``` <details> <summary>Expanded output</summary> ```rust /// My really cool plugic group! /// /// - [`PhysicsPlugin`](physics::PhysicsPlugin) /// - [`RenderingPlugin`](rendering::RenderingPlugin) /// - [`UiPlugin`](ui::UiPlugin) pub struct MyPluginGroup; impl ::bevy_app::PluginGroup for MyPluginGroup { fn build(self) -> ::bevy_app::PluginGroupBuilder { let mut group = ::bevy_app::PluginGroupBuilder::start::<Self>(); { const _: () = { const fn check_default<T: Default>() {} check_default::<physics::PhysicsPlugin>(); }; group = group.add(<physics::PhysicsPlugin>::default()); } { const _: () = { const fn check_default<T: Default>() {} check_default::<rendering::RenderingPlugin>(); }; group = group.add(<rendering::RenderingPlugin>::default()); } { const _: () = { const fn check_default<T: Default>() {} check_default::<ui::UiPlugin>(); }; group = group.add(<ui::UiPlugin>::default()); } group } } ``` </details> --------- Co-authored-by: Doonv <[email protected]> Co-authored-by: Mateusz Wachowiak <[email protected]>
# Objective Right not bevy's task pool abstraction is kind of useless on wasm, since it returns a `FakeTask` which can't be interacted with. This is only good for fire-and-forget it tasks, and isn't even that useful since it's just a thin wrapper around `wasm-bindgen-futures::spawn_local` ## Solution Add a simple `Task<T>` handler type to wasm targets that allow waiting for a task's output or periodically checking for its completion. This PR aims to give the wasm version of these tasks feature parity with the native, multi-threaded version of the task ## Testing - Did you test these changes? *Not yet* --------- Co-authored-by: Periwink <[email protected]> Co-authored-by: Jan Hohenheim <[email protected]>
…d, regions. (bevyengine#14099) Currently, volumetric fog is global and affects the entire scene uniformly. This is inadequate for many use cases, such as local smoke effects. To address this problem, this commit introduces *fog volumes*, which are axis-aligned bounding boxes (AABBs) that specify fog parameters inside their boundaries. Such volumes can also specify a *density texture*, a 3D texture of voxels that specifies the density of the fog at each point. To create a fog volume, add a `FogVolume` component to an entity (which is included in the new `FogVolumeBundle` convenience bundle). Like light probes, a fog volume is conceptually a 1×1×1 cube centered on the origin; a transform can be used to position and resize this region. Many of the fields on the existing `VolumetricFogSettings` have migrated to the new `FogVolume` component. `VolumetricFogSettings` on a camera is still needed to enable volumetric fog. However, by itself `VolumetricFogSettings` is no longer sufficient to enable volumetric fog; a `FogVolume` must be present. Applications that wish to retain the old global fog behavior can simply surround the scene with a large fog volume. By way of implementation, this commit converts the volumetric fog shader from a full-screen shader to one applied to a mesh. The strategy is different depending on whether the camera is inside or outside the fog volume. If the camera is inside the fog volume, the mesh is simply a plane scaled to the viewport, effectively falling back to a full-screen pass. If the camera is outside the fog volume, the mesh is a cube transformed to coincide with the boundaries of the fog volume's AABB. Importantly, in the latter case, only the front faces of the cuboid are rendered. Instead of treating the boundaries of the fog as a sphere centered on the camera position, as we did prior to this patch, we raytrace the far planes of the AABB to determine the portion of each ray contained within the fog volume. We then raymarch in shadow map space as usual. If a density texture is present, we modulate the fixed density value with the trilinearly-interpolated value from that texture. Furthermore, this patch introduces optional jitter to fog volumes, intended for use with TAA. This modifies the position of the ray from frame to frame using interleaved gradient noise, in order to reduce aliasing artifacts. Many implementations of volumetric fog in games use this technique. Note that this patch makes no attempt to write a motion vector; this is because when a view ray intersects multiple voxels there's no single direction of motion. Consequently, fog volumes can have ghosting artifacts, but because fog is "ghostly" by its nature, these artifacts are less objectionable than they would be for opaque objects. A new example, `fog_volumes`, has been added. It demonstrates a single fog volume containing a voxelized representation of the Stanford bunny. The existing `volumetric_fog` example has been updated to use the new local volumetrics API. ## Changelog ### Added * Local `FogVolume`s are now supported, to localize fog to specific regions. They can optionally have 3D density voxel textures for precise control over the distribution of the fog. ### Changed * `VolumetricFogSettings` on a camera no longer enables volumetric fog; instead, it simply enables the processing of `FogVolume`s within the scene. ## Migration Guide * A `FogVolume` is now necessary in order to enable volumetric fog, in addition to `VolumetricFogSettings` on the camera. Existing uses of volumetric fog can be migrated by placing a large `FogVolume` surrounding the scene. --------- Co-authored-by: Alice Cecile <[email protected]> Co-authored-by: François Mockers <[email protected]>
…e#14141) # Objective As mentioned in [this](bevyengine#13152 (comment)) comment, creating a function registry (see bevyengine#14098) is a bit difficult due to the requirements of `DynamicFunction`. Internally, a `DynamicFunction` contains a `Box<dyn FnMut>` (the function that reifies reflected arguments and calls the actual function), which requires `&mut self` in order to be called. This means that users would require a mutable reference to the function registry for it to be useful— which isn't great. And they can't clone the `DynamicFunction` either because cloning an `FnMut` isn't really feasible (wrapping it in an `Arc` would allow it to be cloned but we wouldn't be able to call the clone since we need a mutable reference to the `FnMut`, which we can't get with multiple `Arc`s still alive, requiring us to also slap in a `Mutex`, which adds additional overhead). And we don't want to just replace the `dyn FnMut` with `dyn Fn` as that would prevent reflecting closures that mutate their environment. Instead, we need to introduce a new type to split the requirements of `DynamicFunction`. ## Solution Introduce new types for representing closures. Specifically, this PR introduces `DynamicClosure` and `DynamicClosureMut`. Similar to how `IntoFunction` exists for `DynamicFunction`, two new traits were introduced: `IntoClosure` and `IntoClosureMut`. Now `DynamicFunction` stores a `dyn Fn` with a `'static` lifetime. `DynamicClosure` also uses a `dyn Fn` but has a lifetime, `'env`, tied to its environment. `DynamicClosureMut` is most like the old `DynamicFunction`, keeping the `dyn FnMut` and also typing its lifetime, `'env`, to the environment Here are some comparison tables: | | `DynamicFunction` | `DynamicClosure` | `DynamicClosureMut` | | - | ----------------- | ---------------- | ------------------- | | Callable with `&self` | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ | | Callable with `&mut self` | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | | Allows for non-`'static` lifetimes | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | | | `IntoFunction` | `IntoClosure` | `IntoClosureMut` | | - | -------------- | ------------- | ---------------- | | Convert `fn` functions | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | | Convert `fn` methods | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | | Convert anonymous functions | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | | Convert closures that capture immutable references | ❌ | ✅ | ✅ | | Convert closures that capture mutable references | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ | | Convert closures that capture owned values | ❌[^1] | ✅ | ✅ | [^1]: Due to limitations in Rust, `IntoFunction` can't be implemented for just functions (unless we forced users to manually coerce them to function pointers first). So closures that meet the trait requirements _can technically_ be converted into a `DynamicFunction` as well. To both future-proof and reduce confusion, though, we'll just pretend like this isn't a thing. ```rust let mut list: Vec<i32> = vec![1, 2, 3]; // `replace` is a closure that captures a mutable reference to `list` let mut replace = |index: usize, value: i32| -> i32 { let old_value = list[index]; list[index] = value; old_value }; // Convert the closure into a dynamic closure using `IntoClosureMut::into_closure_mut` let mut func: DynamicClosureMut = replace.into_closure_mut(); // Dynamically call the closure: let args = ArgList::default().push_owned(1_usize).push_owned(-2_i32); let value = func.call_once(args).unwrap().unwrap_owned(); // Check the result: assert_eq!(value.take::<i32>().unwrap(), 2); assert_eq!(list, vec![1, -2, 3]); ``` ### `ReflectFn`/`ReflectFnMut` To make extending the function reflection system easier (the blanket impls for `IntoFunction`, `IntoClosure`, and `IntoClosureMut` are all incredibly short), this PR generalizes callables with two new traits: `ReflectFn` and `ReflectFnMut`. These traits mimic `Fn` and `FnMut` but allow for being called via reflection. In fact, their blanket implementations are identical save for `ReflectFn` being implemented over `Fn` types and `ReflectFnMut` being implemented over `FnMut` types. And just as `Fn` is a subtrait of `FnMut`, `ReflectFn` is a subtrait of `ReflectFnMut`. So anywhere that expects a `ReflectFnMut` can also be given a `ReflectFn`. To reiterate, these traits aren't 100% necessary. They were added in purely for extensibility. If we decide to split things up differently or add new traits/types in the future, then those changes should be much simpler to implement. ### `TypedFunction` Because of the split into `ReflectFn` and `ReflectFnMut`, we needed a new way to access the function type information. This PR moves that concept over into `TypedFunction`. Much like `Typed`, this provides a way to access a function's `FunctionInfo`. By splitting this trait out, it helps to ensure the other traits are focused on a single responsibility. ### Internal Macros The original function PR (bevyengine#13152) implemented `IntoFunction` using a macro which was passed into an `all_tuples!` macro invocation. Because we needed the same functionality for these new traits, this PR has copy+pasted that code for `ReflectFn`, `ReflectFnMut`, and `TypedFunction`— albeit with some differences between them. Originally, I was going to try and macro-ify the impls and where clauses such that we wouldn't have to straight up duplicate a lot of this logic. However, aside from being more complex in general, autocomplete just does not play nice with such heavily nested macros (tried in both RustRover and VSCode). And both of those problems told me that it just wasn't worth it: we need to ensure the crate is easily maintainable, even at the cost of duplicating code. So instead, I made sure to simplify the macro code by removing all fully-qualified syntax and cutting the where clauses down to the bare essentials, which helps to clean up a lot of the visual noise. I also tried my best to document the macro logic in certain areas (I may even add a bit more) to help with maintainability for future devs. ### Documentation Documentation for this module was a bit difficult for me. So many of these traits and types are very interconnected. And each trait/type has subtle differences that make documenting it in a single place, like at the module level, difficult to do cleanly. Describing the valid signatures is also challenging to do well. Hopefully what I have here is okay. I think I did an okay job, but let me know if there any thoughts on ways to improve it. We can also move such a task to a followup PR for more focused discussion. ## Testing You can test locally by running: ``` cargo test --package bevy_reflect ``` --- ## Changelog - Added `DynamicClosure` struct - Added `DynamicClosureMut` struct - Added `IntoClosure` trait - Added `IntoClosureMut` trait - Added `ReflectFn` trait - Added `ReflectFnMut` trait - Added `TypedFunction` trait - `IntoFunction` now only works for standard Rust functions - `IntoFunction` no longer takes a lifetime parameter - `DynamicFunction::call` now only requires `&self` - Removed `DynamicFunction::call_once` - Changed the `IntoReturn::into_return` signature to include a where clause ## Internal Migration Guide > [!important] > Function reflection was introduced as part of the 0.15 dev cycle. This migration guide was written for developers relying on `main` during this cycle, and is not a breaking change coming from 0.14. ### `IntoClosure` `IntoFunction` now only works for standard Rust functions. Calling `IntoFunction::into_function` on a closure that captures references to its environment (either mutable or immutable), will no longer compile. Instead, you will need to use either `IntoClosure::into_closure` to create a `DynamicClosure` or `IntoClosureMut::into_closure_mut` to create a `DynamicClosureMut`, depending on your needs: ```rust let punct = String::from("!"); let print = |value: String| { println!("{value}{punct}"); }; // BEFORE let func: DynamicFunction = print.into_function(); // AFTER let func: DynamicClosure = print.into_closure(); ``` ### `IntoFunction` lifetime Additionally, `IntoFunction` no longer takes a lifetime parameter as it always expects a `'static` lifetime. Usages will need to remove any lifetime parameters: ```rust // BEFORE fn execute<'env, F: IntoFunction<'env, Marker>, Marker>(f: F) {/* ... */} // AFTER fn execute<F: IntoFunction<Marker>, Marker>(f: F) {/* ... */} ``` ### `IntoReturn` `IntoReturn::into_return` now has a where clause. Any manual implementors will need to add this where clause to their implementation.
# Objective
- Continue to pare down the uses on NonSend resources in the engine. In
this case, EventLoopProxy used to be `!Sync`, but is now `Sync` in the
latest version of winit.
## Solution
- New type `EventLoopProxy` as `EventLoopProxyWrapper` to make it into a
normal resource.
- Update the `custom_user_event` example as it no longer needs to
indirectly access the `EventLoopProxy` through a static variable
anymore.
## Testing
- Ran the example. The resource exists just for users to use, so there
aren't any in engine uses for it currently.
---
## Changelog
- make EventLoopProxy into a regular resource.
## Migration Guide
`EventLoopProxy` has been renamed to `EventLoopProxyWrapper` and is now
`Send`, making it an ordinary resource.
Before:
```rust
event_loop_system(event_loop: NonSend<EventLoopProxy<MyEvent>>) {
event_loop.send_event(MyEvent);
}
```
After:
```rust
event_loop_system(event_loop: Res<EventLoopProxy<MyEvent>>) {
event_loop.send_event(MyEvent);
}
```
Reference to bevyengine#14299. # Objective - Ensuring consistent practice of instantiating 3D primitive shapes in Bevy. ## Solution - Add `new` method, containing `radius` and `height` arguments, to Cone 3D primitive shape. ## Testing - Instantiated cone using same values (radius is `2.` and height is `5.`), using the current method and the added `new` method. - Basic setup of Bevy Default Plugins and `3DCameraBundle`. --- ## Showcase <details> <summary>Click to view showcase</summary> ```rust use bevy::prelude::*; fn main() { App::new() .add_plugins(DefaultPlugins) .add_systems(Startup, setup) .run(); } fn setup( mut commands: Commands, mut meshes: ResMut<Assets<Mesh>>, mut materials: ResMut<Assets<StandardMaterial>>, ) { let new_cone = meshes.add(Cone::new(2., 5.)); commands.spawn(PbrBundle { mesh: new_cone, ..default() }); let old_cone = meshes.add(Cone { radius: 2., height: 5., }); commands.spawn(PbrBundle { mesh: old_cone, material: materials.add(Color::WHITE), transform: Transform::from_xyz(10., 0., 0.), ..default() }); commands.spawn(Camera3dBundle { transform: Transform::from_xyz(20., 20., 20.).looking_at(Vec3::ZERO, Dir3::Y), ..default() }); } ``` </details>  - Pink Cone is created using the `new` method. - Black Cone is created using the existing method. ## Migration Guide - Addition of `new` method to the 3D primitive Cone struct.
# Objective
Many functions can be converted to `DynamicFunction` using
`IntoFunction`. Unfortunately, we are limited by Rust itself and the
implementations are far from exhaustive. For example, we can't convert
functions with more than 16 arguments. Additionally, we can't handle
returns with lifetimes not tied to the lifetime of the first argument.
In such cases, users will have to create their `DynamicFunction`
manually.
Let's take the following function:
```rust
fn get(index: usize, list: &Vec<String>) -> &String {
&list[index]
}
```
This function cannot be converted to a `DynamicFunction` via
`IntoFunction` due to the lifetime of the return value being tied to the
second argument. Therefore, we need to construct the `DynamicFunction`
manually:
```rust
DynamicFunction::new(
|mut args, info| {
let list = args
.pop()
.unwrap()
.take_ref::<Vec<String>>(&info.args()[1])?;
let index = args.pop().unwrap().take_owned::<usize>(&info.args()[0])?;
Ok(Return::Ref(get(index, list)))
},
FunctionInfo::new()
.with_name("get")
.with_args(vec![
ArgInfo::new::<usize>(0).with_name("index"),
ArgInfo::new::<&Vec<String>>(1).with_name("list"),
])
.with_return_info(ReturnInfo::new::<&String>()),
);
```
While still a small and straightforward snippet, there's a decent amount
going on here. There's a lot of room for improvements when it comes to
ergonomics and readability.
The goal of this PR is to address those issues.
## Solution
Improve the ergonomics and readability of manually created
`DynamicFunction`s.
Some of the major changes:
1. Removed the need for `&ArgInfo` when reifying arguments (i.e. the
`&info.args()[1]` calls)
2. Added additional `pop` methods on `ArgList` to handle both popping
and casting
3. Added `take` methods on `ArgList` for taking the arguments out in
order
4. Removed the need for `&FunctionInfo` in the internal closure (Change
1 made it no longer necessary)
5. Added methods to automatically handle generating `ArgInfo` and
`ReturnInfo`
With all these changes in place, we get something a lot nicer to both
write and look at:
```rust
DynamicFunction::new(
|mut args| {
let index = args.take::<usize>()?;
let list = args.take::<&Vec<String>>()?;
Ok(Return::Ref(get(index, list)))
},
FunctionInfo::new()
.with_name("get")
.with_arg::<usize>("index")
.with_arg::<&Vec<String>>("list")
.with_return::<&String>(),
);
```
Alternatively, to rely on type inference for taking arguments, you could
do:
```rust
DynamicFunction::new(
|mut args| {
let index = args.take_owned()?;
let list = args.take_ref()?;
Ok(Return::Ref(get(index, list)))
},
FunctionInfo::new()
.with_name("get")
.with_arg::<usize>("index")
.with_arg::<&Vec<String>>("list")
.with_return::<&String>(),
);
```
## Testing
You can test locally by running:
```
cargo test --package bevy_reflect
```
---
## Changelog
- Removed `&ArgInfo` argument from `FromArg::from_arg` trait method
- Removed `&ArgInfo` argument from `Arg::take_***` methods
- Added `ArgValue`
- `Arg` is now a struct containing an `ArgValue` and an argument `index`
- `Arg::take_***` methods now require `T` is also `TypePath`
- Added `Arg::new`, `Arg::index`, `Arg::value`, `Arg::take_value`, and
`Arg::take` methods
- Replaced `ArgId` in `ArgError` with just the argument `index`
- Added `ArgError::EmptyArgList`
- Renamed `ArgList::push` to `ArgList::push_arg`
- Added `ArgList::pop_arg`, `ArgList::pop_owned`, `ArgList::pop_ref`,
and `ArgList::pop_mut`
- Added `ArgList::take_arg`, `ArgList::take_owned`, `ArgList::take_ref`,
`ArgList::take_mut`, and `ArgList::take`
- `ArgList::pop` is now generic
- Renamed `FunctionError::InvalidArgCount` to
`FunctionError::ArgCountMismatch`
- The closure given to `DynamicFunction::new` no longer has a
`&FunctionInfo` argument
- Added `FunctionInfo::with_arg`
- Added `FunctionInfo::with_return`
## Internal Migration Guide
> [!important]
> Function reflection was introduced as part of the 0.15 dev cycle. This
migration guide was written for developers relying on `main` during this
cycle, and is not a breaking change coming from 0.14.
* The `FromArg::from_arg` trait method and the `Arg::take_***` methods
no longer take a `&ArgInfo` argument.
* What used to be `Arg` is now `ArgValue`. `Arg` is now a struct which
contains an `ArgValue`.
* `Arg::take_***` methods now require `T` is also `TypePath`
* Instances of `id: ArgId` in `ArgError` have been replaced with `index:
usize`
* `ArgList::push` is now `ArgList::push_arg`. It also takes the new
`ArgValue` type.
* `ArgList::pop` has become `ArgList::pop_arg` and now returns
`ArgValue`. `Arg::pop` now takes a generic type and downcasts to that
type. It's recommended to use `ArgList::take` and friends instead since
they allow removing the arguments from the list in the order they were
pushed (rather than reverse order).
* `FunctionError::InvalidArgCount` is now
`FunctionError::ArgCountMismatch`
* The closure given to `DynamicFunction::new` no longer has a
`&FunctionInfo` argument. This argument can be removed.
…ine (bevyengine#14347) # Objective The robots.txt file for the [dev docs](https://dev-docs.bevyengine.org) looks like this `User-Agent: *\nDisallow: /` It should look like this ``` User-Agent: * Disallow: / ``` ## Solution Use [`ANSI-C`](https://www.gnu.org/software/bash/manual/bash.html#ANSI_002dC-Quoting) quoting to properly handle the `\n` ## Testing - [x] Run the fixed echo command in local terminal. - [ ] Wait for the dev doces to deploy and observe if the mistake has been fixed
…bevyengine#14257) This commit uses the [`offset-allocator`] crate to combine vertex and index arrays from different meshes into single buffers. Since the primary source of `wgpu` overhead is from validation and synchronization when switching buffers, this significantly improves Bevy's rendering performance on many scenes. This patch is a more flexible version of bevyengine#13218, which also used slabs. Unlike bevyengine#13218, which used slabs of a fixed size, this commit implements slabs that start small and can grow. In addition to reducing memory usage, supporting slab growth reduces the number of vertex and index buffer switches that need to happen during rendering, leading to improved performance. To prevent pathological fragmentation behavior, slabs are capped to a maximum size, and mesh arrays that are too large get their own dedicated slabs. As an additional improvement over bevyengine#13218, this commit allows the application to customize all allocator heuristics. The `MeshAllocatorSettings` resource contains values that adjust the minimum and maximum slab sizes, the cutoff point at which meshes get their own dedicated slabs, and the rate at which slabs grow. Hopefully-sensible defaults have been chosen for each value. Unfortunately, WebGL 2 doesn't support the *base vertex* feature, which is necessary to pack vertex arrays from different meshes into the same buffer. `wgpu` represents this restriction as the downlevel flag `BASE_VERTEX`. This patch detects that bit and ensures that all vertex buffers get dedicated slabs on that platform. Even on WebGL 2, though, we can combine all *index* arrays into single buffers to reduce buffer changes, and we do so. The following measurements are on Bistro: Overall frame time improves from 8.74 ms to 5.53 ms (1.58x speedup): 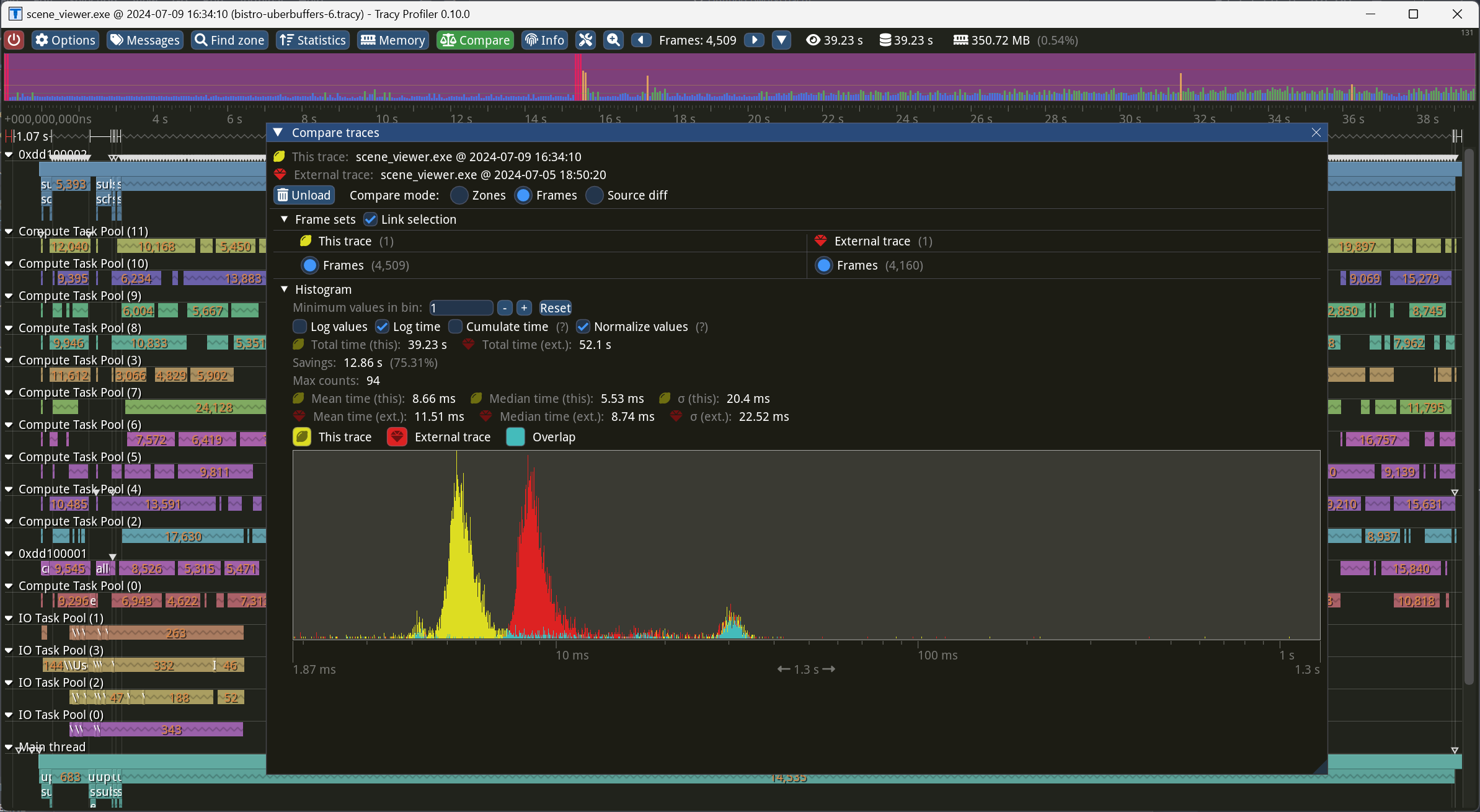 Render system time improves from 6.57 ms to 3.54 ms (1.86x speedup):  Opaque pass time improves from 4.64 ms to 2.33 ms (1.99x speedup):  ## Migration Guide ### Changed * Vertex and index buffers for meshes may now be packed alongside other buffers, for performance. * `GpuMesh` has been renamed to `RenderMesh`, to reflect the fact that it no longer directly stores handles to GPU objects. * Because meshes no longer have their own vertex and index buffers, the responsibility for the buffers has moved from `GpuMesh` (now called `RenderMesh`) to the `MeshAllocator` resource. To access the vertex data for a mesh, use `MeshAllocator::mesh_vertex_slice`. To access the index data for a mesh, use `MeshAllocator::mesh_index_slice`. [`offset-allocator`]: https://github.com/pcwalton/offset-allocator
# Objective - bevyengine#14193 changed the bunny meshlet url but didn't update example metadata ## Solution - Also update the url there
…#14354) # Objective - Fixes bevyengine#14333 ## Solution - Updated `trigger_observers` signature to operate over a slice instead of an `Iterator`. - Updated calls to `trigger_observers` to match the new signature. --- ## Migration Guide - TBD
# Objective
Fill a gap in the functionality of our curve constructions by allowing
users to easily build cyclic curves from control data.
## Solution
Here I opted for something lightweight and discoverable. There is a new
`CyclicCubicGenerator` trait with a method `to_curve_cyclic` which uses
splines' control data to create curves that are cyclic. For now, its
signature is exactly like that of `CubicGenerator` — `to_curve_cyclic`
just yields a `CubicCurve`:
```rust
/// Implement this on cubic splines that can generate a cyclic cubic curve from their spline parameters.
///
/// This makes sense only when the control data can be interpreted cyclically.
pub trait CyclicCubicGenerator<P: VectorSpace> {
/// Build a cyclic [`CubicCurve`] by computing the interpolation coefficients for each curve segment.
fn to_curve_cyclic(&self) -> CubicCurve<P>;
}
```
This trait has been implemented for `CubicHermite`,
`CubicCardinalSpline`, `CubicBSpline`, and `LinearSpline`:
<img width="753" alt="Screenshot 2024-07-01 at 8 58 27 PM"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/2975848/69ae0802-3b78-4fb9-b73a-6f842cf3b33c">
<img width="628" alt="Screenshot 2024-07-01 at 9 00 14 PM"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/2975848/2992175a-a96c-40fc-b1a1-5206c3572cde">
<img width="606" alt="Screenshot 2024-07-01 at 8 59 36 PM"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/2975848/9e99eb3a-dbe6-42da-886c-3d3e00410d03">
<img width="603" alt="Screenshot 2024-07-01 at 8 59 01 PM"
src="https://github.com/bevyengine/bevy/assets/2975848/d037bc0c-396a-43af-ab5c-fad9a29417ef">
(Each type pictured respectively with the control points rendered as
green spheres; tangents not pictured in the case of the Hermite spline.)
These curves are all parametrized so that the output of `to_curve` and
the output of `to_curve_cyclic` are similar. For instance, in
`CubicCardinalSpline`, the first output segment is a curve segment
joining the first and second control points in each, although it is
constructed differently. In the other cases, the segments from
`to_curve` are a subset of those in `to_curve_cyclic`, with the new
segments appearing at the end.
## Testing
I rendered cyclic splines from control data and made sure they looked
reasonable. Existing tests are intact for splines where previous code
was modified. (Note that the coefficient computation for cyclic spline
segments is almost verbatim identical to that of their non-cyclic
counterparts.)
The Bezier benchmarks also look fine.
---
## Changelog
- Added `CyclicCubicGenerator` trait to `bevy_math::cubic_splines` for
creating cyclic curves from control data.
- Implemented `CyclicCubicGenerator` for `CubicHermite`,
`CubicCardinalSpline`, `CubicBSpline`, and `LinearSpline`.
- `bevy_math` now depends on `itertools`.
---
## Discussion
### Design decisions
The biggest thing here is just the approach taken in the first place:
namely, the cyclic constructions use new methods on the same old
structs. This choice was made to reduce friction and increase
discoverability but also because creating new ones just seemed
unnecessary: the underlying data would have been the same, so creating
something like "`CyclicCubicBSpline`" whose internally-held control data
is regarded as cyclic in nature doesn't really accomplish much — the end
result for the user is basically the same either way.
Similarly, I don't presently see a pressing need for `to_curve_cyclic`
to output something other than a `CubicCurve`, although changing this in
the future may be useful. See below.
A notable omission here is that `CyclicCubicGenerator` is not
implemented for `CubicBezier`. This is not a gap waiting to be filled —
`CubicBezier` just doesn't have enough data to join its start with its
end without just making up the requisite control points wholesale. In
all the cases where `CyclicCubicGenerator` has been implemented here,
the fashion in which the ends are connected is quite natural and follows
the semantics of the associated spline construction.
### Future direction
There are two main things here:
1. We should investigate whether we should do something similar for
NURBS. I just don't know that much about NURBS at the moment, so I
regarded this as out of scope for the PR.
2. We may eventually want to change the output type of
`CyclicCubicGenerator::to_curve_cyclic` to a type which reifies the
cyclic nature of the curve output. This wasn't done in this PR because
I'm unsure how much value a type-level guarantee of cyclicity actually
has, but if some useful features make sense only in the case of cyclic
curves, this might be worth pursuing.
# Objective - `CameraRenderGraph` is not inspectable via reflection, but should be (the name of the configured render graph should be visible in editors, etc.) ## Solution - Derive and reflect `Debug` for `CameraRenderGraph`
Progress towards bevyengine#7386. Following discussion https://discord.com/channels/691052431525675048/1253260494538539048/1253387942311886960 This Pull Request adds an example to detect system order ambiguities, and also asserts none exist. A lot of schedules are ignored in ordered to have the test passing, we should thrive to make them pass, but in other pull requests. <details><summary>example output <b>summary</b>, without ignored schedules</summary> <p> ```txt $ cargo run --example ambiguity_detection 2>&1 | grep -C 1 "pairs of syst" 2024-06-21T13:17:55.776585Z WARN bevy_ecs::schedule::schedule: Schedule First has ambiguities. 1 pairs of systems with conflicting data access have indeterminate execution order. Consider adding `before`, `after`, or `ambiguous_with` relationships between these: -- bevy_time::time_system (in set TimeSystem) and bevy_ecs::event::event_update_system (in set EventUpdates) -- 2024-06-21T13:17:55.782265Z WARN bevy_ecs::schedule::schedule: Schedule PreUpdate has ambiguities. 11 pairs of systems with conflicting data access have indeterminate execution order. Consider adding `before`, `after`, or `ambiguous_with` relationships between these: -- bevy_pbr::prepass::update_mesh_previous_global_transforms and bevy_asset::server::handle_internal_asset_events -- 2024-06-21T13:17:55.809516Z WARN bevy_ecs::schedule::schedule: Schedule PostUpdate has ambiguities. 63 pairs of systems with conflicting data access have indeterminate execution order. Consider adding `before`, `after`, or `ambiguous_with` relationships between these: -- bevy_ui::accessibility::image_changed and bevy_ecs::schedule::executor::apply_deferred -- 2024-06-21T13:17:55.816287Z WARN bevy_ecs::schedule::schedule: Schedule Last has ambiguities. 3 pairs of systems with conflicting data access have indeterminate execution order. Consider adding `before`, `after`, or `ambiguous_with` relationships between these: -- bevy_gizmos::update_gizmo_meshes<bevy_gizmos::aabb::AabbGizmoConfigGroup> (in set UpdateGizmoMeshes) and bevy_gizmos::update_gizmo_meshes<bevy_gizmos::light::LightGizmoConfigGroup> (in set UpdateGizmoMeshes) -- 2024-06-21T13:17:55.831074Z WARN bevy_ecs::schedule::schedule: Schedule ExtractSchedule has ambiguities. 296 pairs of systems with conflicting data access have indeterminate execution order. Consider adding `before`, `after`, or `ambiguous_with` relationships between these: -- bevy_render::extract_component::extract_components<bevy_sprite::SpriteSource> and bevy_render::render_asset::extract_render_asset<bevy_sprite::mesh2d::material::PreparedMaterial2d<bevy_sprite::mesh2d::color_material::ColorMaterial>> ``` </p> </details> To try locally: ```sh CI_TESTING_CONFIG="./.github/example-run/ambiguity_detection.ron" cargo run --example ambiguity_detection --features "bevy_ci_testing,trace,trace_chrome" ``` --------- Co-authored-by: Jan Hohenheim <[email protected]>
# Objective When using tracing or [`bevy_mod_debugdump`](https://github.com/jakobhellermann/bevy_mod_debugdump), the names of function systems produced by closures are either ambiguous (like `game::mainapp::{closure}` when tracing) or too long (`bevy_mod_debugdump` includes full type signature if no name given), which makes debugging with tracing difficult. ## Solution Add a function `with_name` to rename a system. The proposed API can be used in the following way: ```rust app .add_systems(Startup, IntoSystem::into_system(|name: SystemName| { println!("System name: {}", name.name().to_owned()); }).with_name("print_test_system")); ``` ## Testing - There is a test in `bevy_ecs::system:system_name::test_closure_system_name_regular_param`
# Objective - The event propagation benchmark is largely derived from bevy_eventlistener. However, it doesn't accurately reflect performance of bevy side, as our event bubble propagation is based on observer. ## Solution - added several new benchmarks that focuse on observer itself rather than event bubble
…engine#14390) Due to a bug in `load_gltf`, the `GltfNode::children` links of each node actually point to the node itself, rather than to the node's children. This commit fixes that bug. Note that this didn't affect the scene hierarchy of the instantiated glTF, only the hierarchy as present in the `GltfNode` assets. This is likely why the bug was never noticed until now.
# Objective Fixes bevyengine#14386 ## Solution - Added the `#[deprecate]` attribute to the `is_playing_animation` function. ## Testing The project successfully builds. --- ## Migration Guide The user will just need to replace functions named `is_playing_animation` with `animation_is_playing`.
# Objective - Fixes: bevyengine#14036 ## Solution - Add a world space transformation for the environment sample direction. ## Testing - I have tested the newly added `transform` field using the newly added `rotate_environment_map` example. https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/2de77c65-14bc-48ee-b76a-fb4e9782dbdb ## Migration Guide - Since we have added a new filed to the `EnvironmentMapLight` struct, users will need to include `..default()` or some rotation value in their initialization code.
# Objective - The current default viewport crashes bevy due to a wgpu validation error, this PR fixes that - Fixes bevyengine#14355 ## Solution - `Viewport::default()` now returns a 1x1 viewport ## Testing - I modified the `3d_viewport_to_world` example to use `Viewport::default()`, and it works as expected (only the top-left pixel is rendered)
# Objective Fixes bevyengine#7433 Alternative to bevyengine#14323 ## Solution Add `DefaultPlugins` so we actually have tracing spans when using `trace_tracy` or `trace_chrome`. ## Testing ``` cargo run --release --features trace_tracy --example transform_hierarchy large_tree ``` This now connects to Tracy and sends a bunch of data.
# Objective When the user renders multiple cameras to the same output texture, it can sometimes be confusing what `ClearColorConfig` is necessary for each camera to avoid overwriting the previous camera's output. This is particular true in cases where the user uses mixed HDR cameras, which means that their scene is being rendered to different internal textures. ## Solution When a view has a configured viewport, set the GPU scissor in the upscaling node so we don't overwrite areas that were written to by other cameras. ## Testing Ran the `split_screen` example.
# Objective
Fixes the buttons in `split_screen` touching the edge of the viewport.
## Solution
This seems like it might potentially be "normal css-like" behavior with
absolutely positioned nodes and padding.
<details>
<summary>HTML test</summary>
```html
<html>
<body>
<div style="width: 100%; height: 100%; padding: 20px;">
<div style="width: 100%; height: 100%; padding: 20px; display: flex; justify-content: space-between; align-items: center">
<div style="width: 40px; height: 40px; border: 1px solid black;"><</div>
<div style="width: 40px; height: 40px; border: 1px solid black;">></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
```
</details>
Instead I just removed the padding from the root node.
## Testing
Added ui debug gizmos to the example and checked before/after.
Before:
<img width="1280" alt="Screenshot 2024-07-20 at 9 23 09 AM"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/f3cac637-8de9-4acf-bb13-994791998bb7">
After:
<img width="1280" alt="Screenshot 2024-07-20 at 9 37 27 AM"
src="https://github.com/user-attachments/assets/4d3c23b4-5a48-45da-b8a5-a394fd34a44b">
# Objective
- Building bevy_gltf with feature dds fails:
```
> cargo build -p bevy_gltf --features dds
Compiling bevy_core_pipeline v0.15.0-dev (crates/bevy_core_pipeline)
error[E0061]: this function takes 7 arguments but 6 arguments were supplied
--> crates/bevy_core_pipeline/src/tonemapping/mod.rs:442:5
|
442 | Image::from_buffer(
| ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
...
445 | bytes,
| ----- an argument of type `std::string::String` is missing
|
note: associated function defined here
--> crates/bevy_render/src/texture/image.rs:709:12
|
709 | pub fn from_buffer(
| ^^^^^^^^^^^
help: provide the argument
|
442 | Image::from_buffer(/* std::string::String */, bytes, image_type, CompressedImageFormats::NONE, false, image_sampler, RenderAssetUsages::RENDER_WORLD)
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
For more information about this error, try `rustc --explain E0061`.
error: could not compile `bevy_core_pipeline` (lib) due to 1 previous error
```
- If you're fixing a specific issue, say "Fixes #X".
## Solution
- enable dds feature in bevy_core_pipeline
## Testing
- `cargo build -p bevy_gltf --features dds`
# Objective - Replacing CAS with Cas in CASPlugin - Closes bevyengine#14341 ## Solution - Simple replace --------- Co-authored-by: François Mockers <[email protected]> Co-authored-by: Jan Hohenheim <[email protected]> Co-authored-by: François Mockers <[email protected]>
Sign up for free
to join this conversation on GitHub.
Already have an account?
Sign in to comment
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
This suggestion is invalid because no changes were made to the code.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is closed.
Suggestions cannot be applied while viewing a subset of changes.
Only one suggestion per line can be applied in a batch.
Add this suggestion to a batch that can be applied as a single commit.
Applying suggestions on deleted lines is not supported.
You must change the existing code in this line in order to create a valid suggestion.
Outdated suggestions cannot be applied.
This suggestion has been applied or marked resolved.
Suggestions cannot be applied from pending reviews.
Suggestions cannot be applied on multi-line comments.
Suggestions cannot be applied while the pull request is queued to merge.
Suggestion cannot be applied right now. Please check back later.
Tested the following still work that had merge conflicts:
deferred_renderingtransparency_2dcustom_phase_itemWill do a once-over on the actual upstream PR diff once merged.