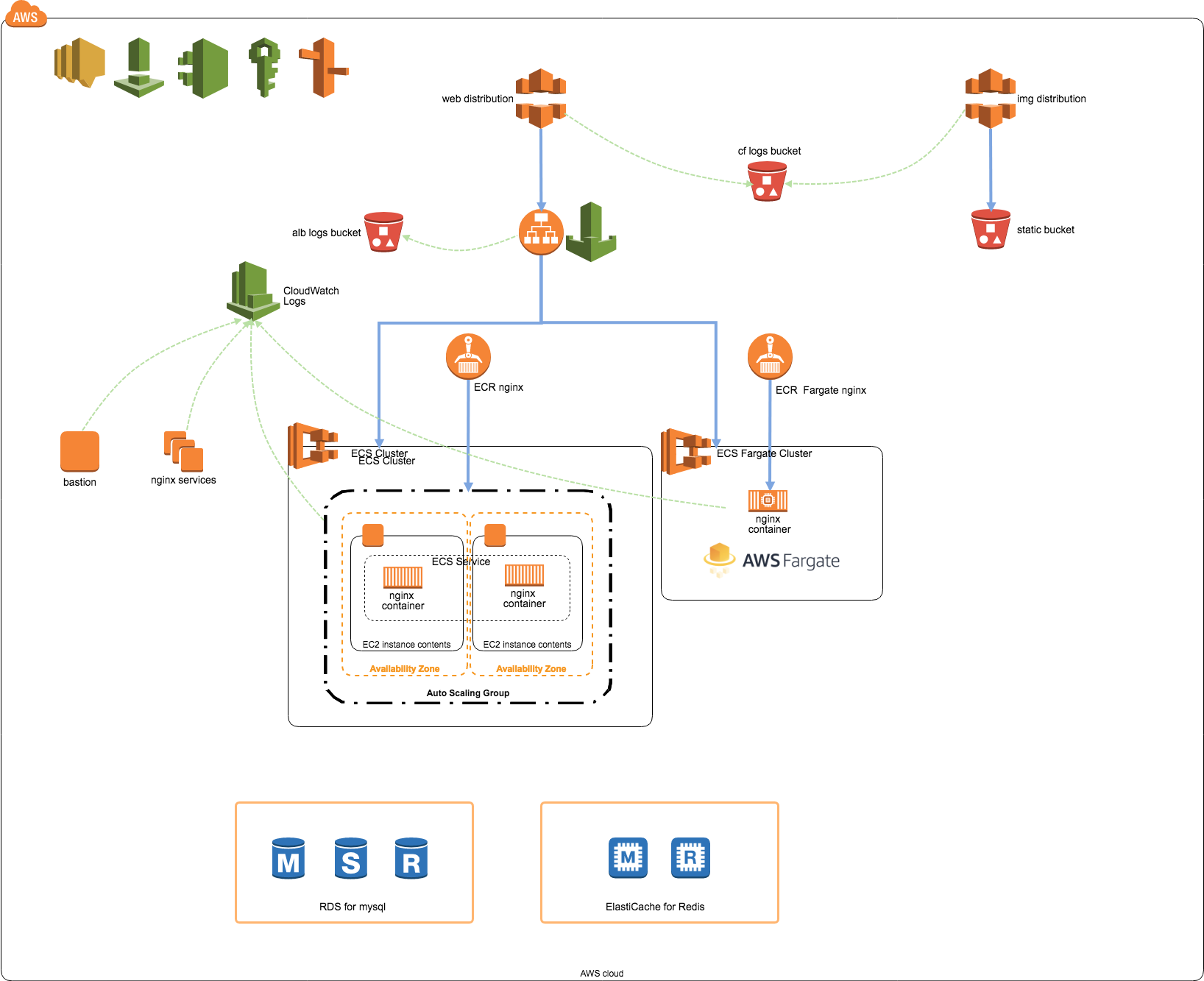
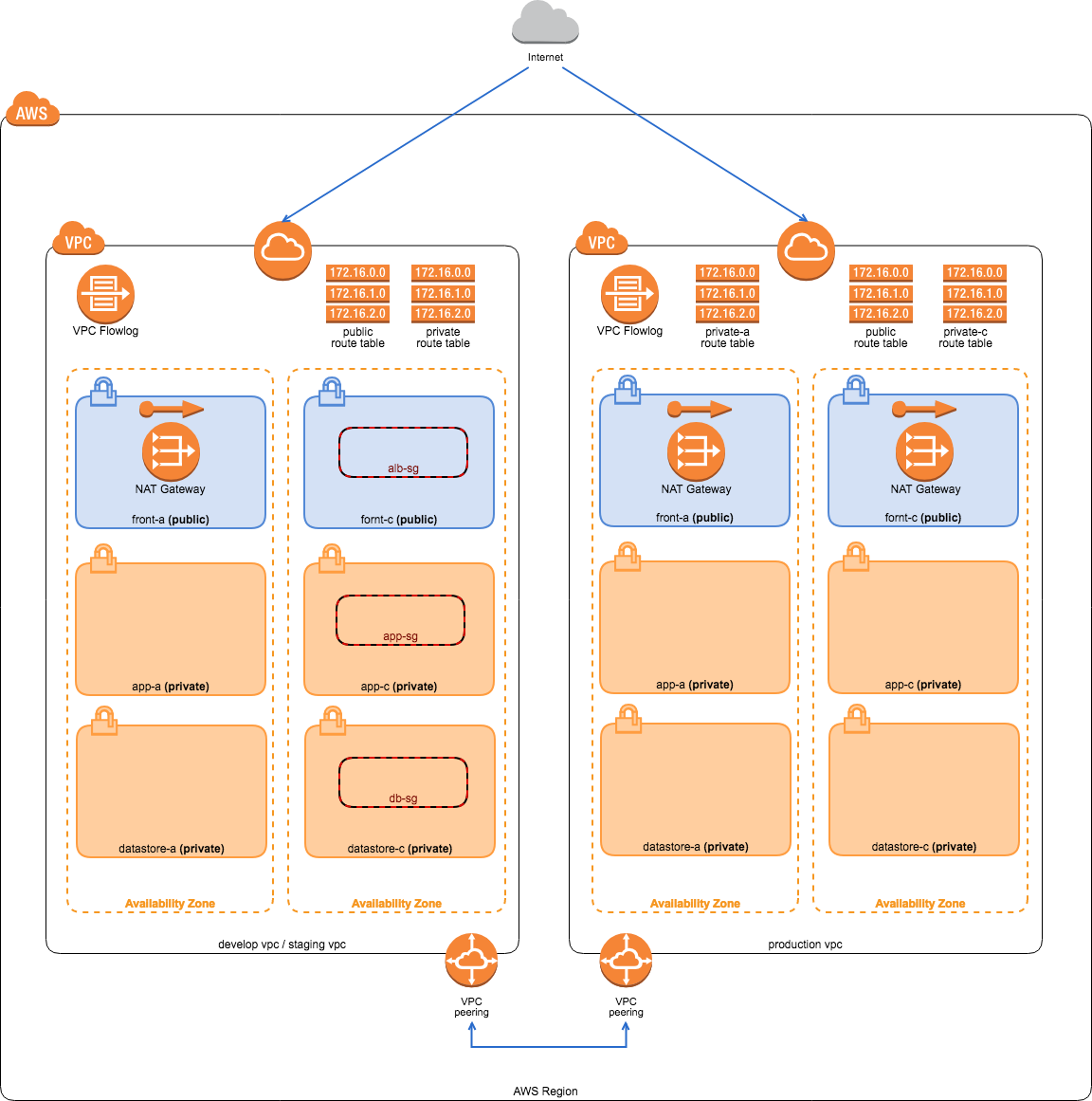
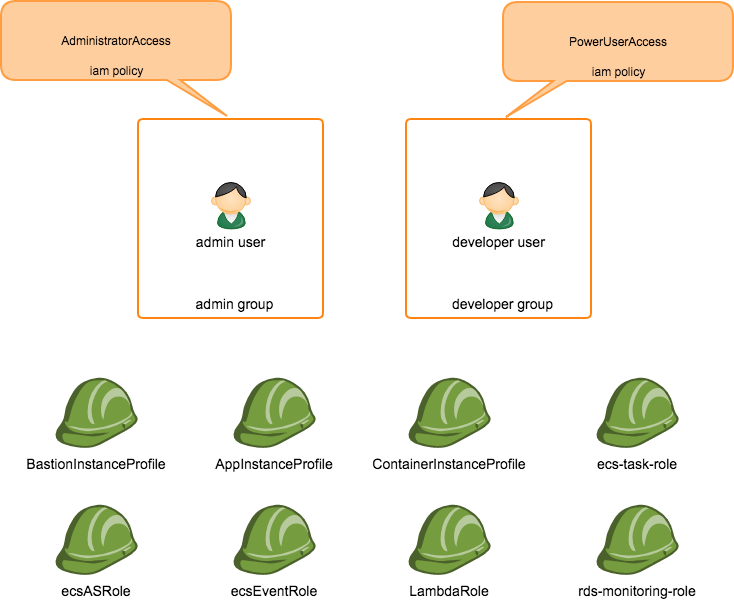
Mac OS High Sierra 10.13.6Terraform v0.11.8aws-cli/1.16.13 Python/3.6.2 Darwin/17.7.0 botocore/1.12.3
Please refer to this link
https://github.com/awslabs/git-secrets
Execute this command in the repository directory of github.
$ git secrets --install
✓ Installed commit-msg hook to .git/hooks/commit-msg
✓ Installed pre-commit hook to .git/hooks/pre-commit
✓ Installed prepare-commit-msg hook to .git/hooks/prepare-commit-msg
Please refer to this link
https://github.com/aws/aws-cli
If you are using Homebrew, there is also such a method.
brew install awscli
The way to check the installed version is to run this command.
$ aws --version
aws-cli/1.16.13 Python/3.6.2 Darwin/17.7.0 botocore/1.12.3
Execute this command to set aws-cli.
In doing so, you need the IAM account access key and secret key.
Unless otherwise specified, Region is set to ap-northeast-1 and Output is set to json
$ aws configure --profile user1
AWS Access Key ID [None]: {your IAM account access key}
AWS Secret Access Key [None]: {your IAM account secret key}
Default region name [None]: ap-northeast-1
Default output format [None]: json
install Terraform on Mac.Download binary package for macOS from here.
$ mkdir ~/terraform
$ cd ~/terraform
$ curl -sL https://releases.hashicorp.com/terraform/0.11.8/terraform_0.11.8_darwin_amd64.zip > terraform.zip
$ unzip terraform.zip
Archive: terraform.zip
inflating: terraform
$ export PATH=$PATH:~/terraform/
I think that the path finished by this, try running the terraform command. Installation is complete.
$ terraform
Usage: terraform [-version] [-help] <command> [args]
The available commands for execution are listed below.
The most common, useful commands are shown first, followed by
less common or more advanced commands. If you're just getting
started with Terraform, stick with the common commands. For the
other commands, please read the help and docs before usage.
Common commands:
apply Builds or changes infrastructure
console Interactive console for Terraform interpolations
destroy Destroy Terraform-managed infrastructure
env Workspace management
fmt Rewrites config files to canonical format
get Download and install modules for the configuration
graph Create a visual graph of Terraform resources
import Import existing infrastructure into Terraform
init Initialize a Terraform working directory
output Read an output from a state file
plan Generate and show an execution plan
providers Prints a tree of the providers used in the configuration
push Upload this Terraform module to Atlas to run
refresh Update local state file against real resources
show Inspect Terraform state or plan
taint Manually mark a resource for recreation
untaint Manually unmark a resource as tainted
validate Validates the Terraform files
version Prints the Terraform version
workspace Workspace management
All other commands:
debug Debug output management (experimental)
force-unlock Manually unlock the terraform state
state Advanced state management
The way to check the installed version is to run this command.
$ terraform -v
Terraform v0.11.8
create a bucket to save tfsatefile.

aws s3 --profile {your aws-cli profile} --region ap-northeast-1 mb s3://{bucket name}
aws s3 --profile {your aws-cli profile} --region ap-northeast-1 ls | grep {bucket name}
$ make init ENV={env} REGION=ap-northeast-1 BUCKET_NAME={bucket name} PROFILE={your aws-cli profile}
$ make plan ENV={env} REGION=ap-northeast-1 BUCKET_NAME={bucket name} PROFILE={your aws-cli profile}
$ make apply ENV={env} REGION=ap-northeast-1 BUCKET_NAME={bucket name} PROFILE={your aws-cli profile}
$ make destroy ENV={env} REGION=ap-northeast-1 BUCKET_NAME={bucket name} PROFILE={your aws-cli profile}
Takayuki Niinuma
GitHub : @monstar-taka