CogVideoX/CogVideoX1.5 is a model that converts text/image to video. xDiT currently integrates USP technology (including Ulysses Attention and Ring Attention) and CFG parallel processing to improve inference speed, while work on PipeFusion is ongoing.
We conducted a thorough analysis of the performance differences between a single GPU CogVideoX inference based on the diffusers library and our proposed parallel version when generating a 49-frame (6-second) 720x480 resolution video. We can combine different parallel methods arbitrarily to achieve varying performance. In this paper, we systematically tested the acceleration performance of xDiT on 1-12 L40 (PCIe) GPUs.
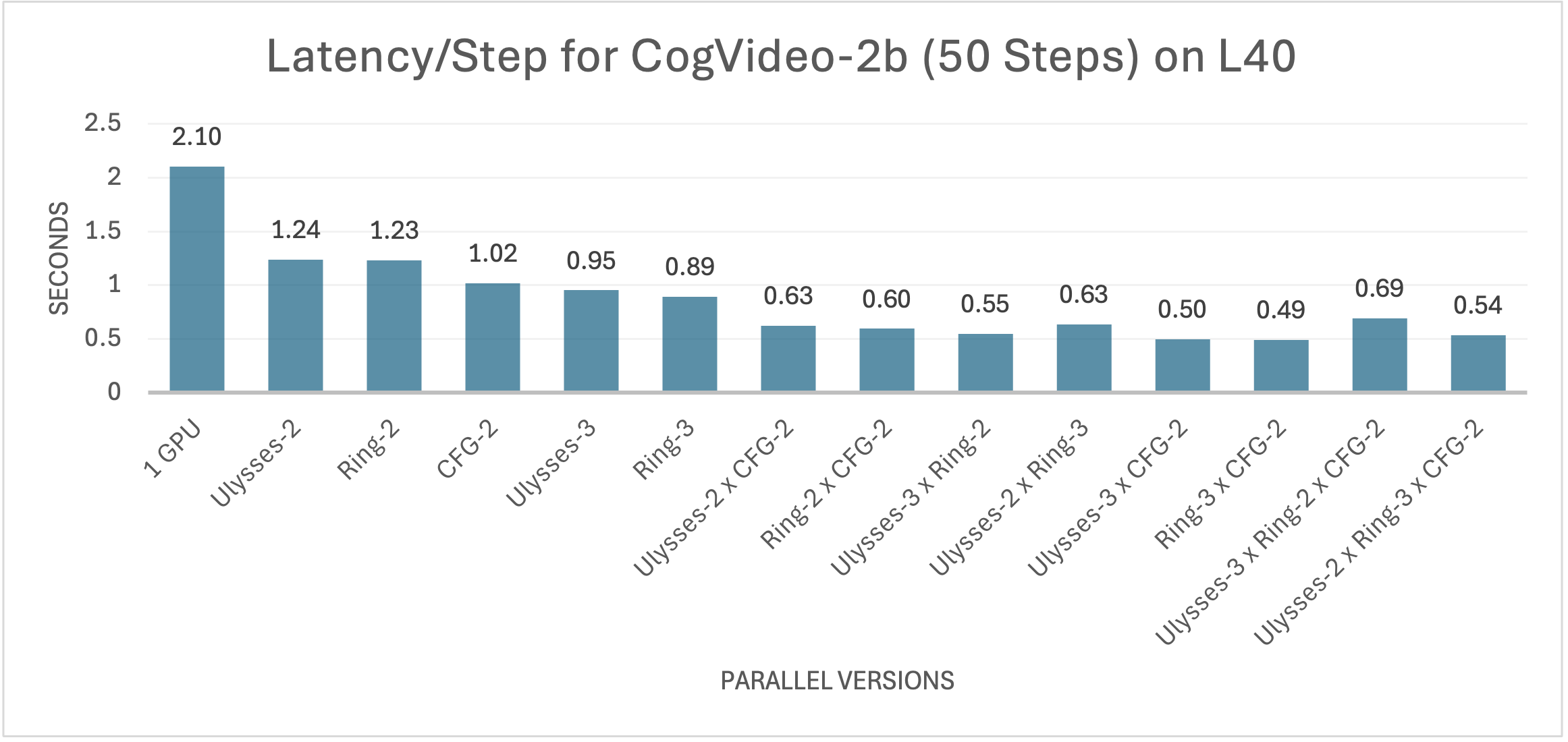
As shown in the figures, for the base model CogVideoX-2b, significant reductions in inference latency were observed whether using Ulysses Attention, Ring Attention, or Classifier-Free Guidance (CFG) parallel processing. It is noteworthy that due to its lower communication overhead, the CFG parallel method outperforms the other two technologies in terms of performance. By combining sequential parallelism and CFG parallelism, we successfully increased inference efficiency. With increasing parallelism, the inference latency continues to decrease. In the optimal configuration, xDiT achieves a 4.29x acceleration relative to single GPU inference, reducing the time for each iteration to just 0.49 seconds. Given the default 50 iterations of CogVideoX, the end-to-end generation of a 24.5-second video can be completed in a total of 30 seconds.
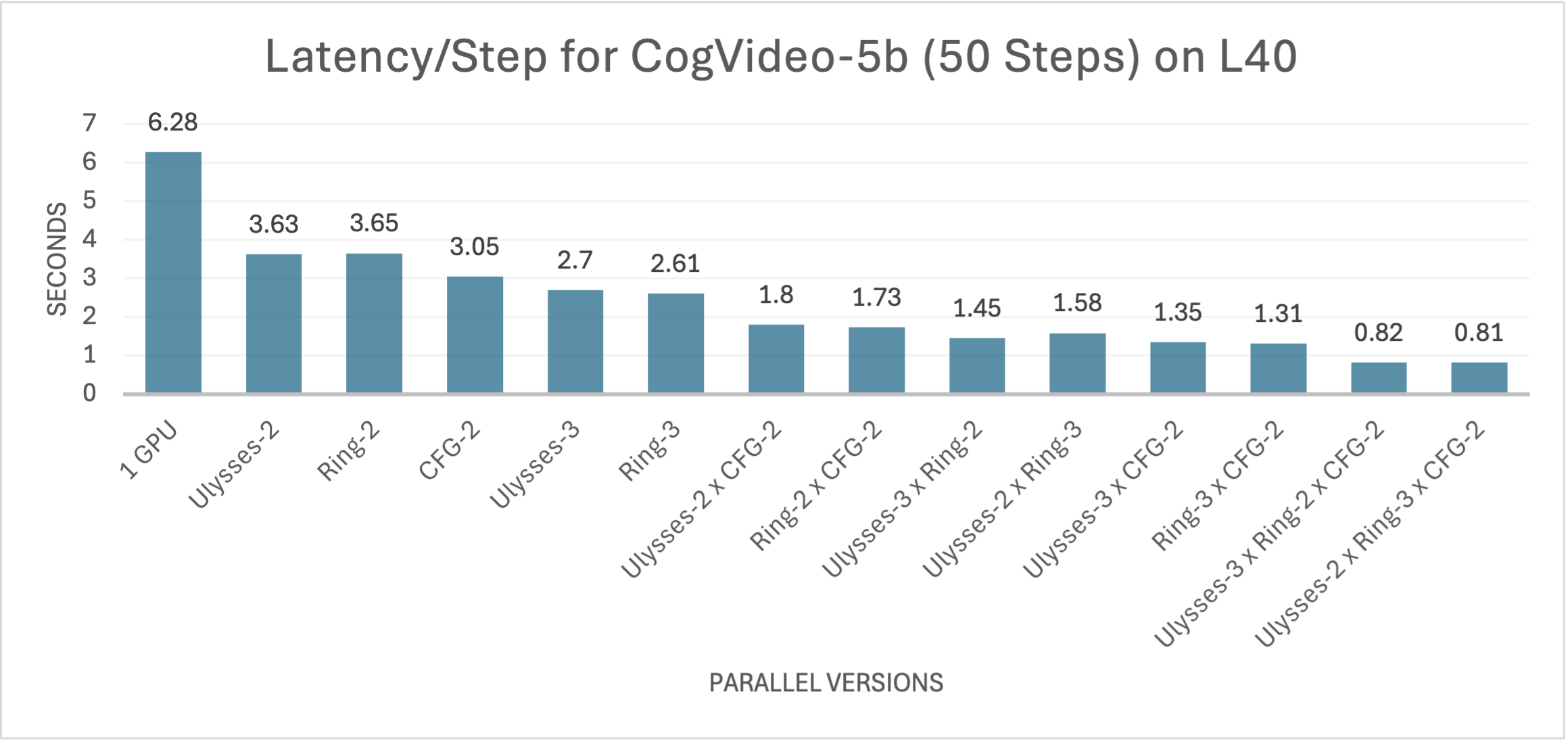
For the more complex CogVideoX-5b model, although increasing parameters to enhance video quality and visual effects leads to a significant rise in computational costs, all methods maintain similar performance trends to CogVideoX-2b on this model, with further improvements in the acceleration effects of the parallel versions. Compared to the single GPU version, xDiT achieves up to a 7.75x increase in inference speed, reducing the end-to-end video generation time to around 40 seconds.
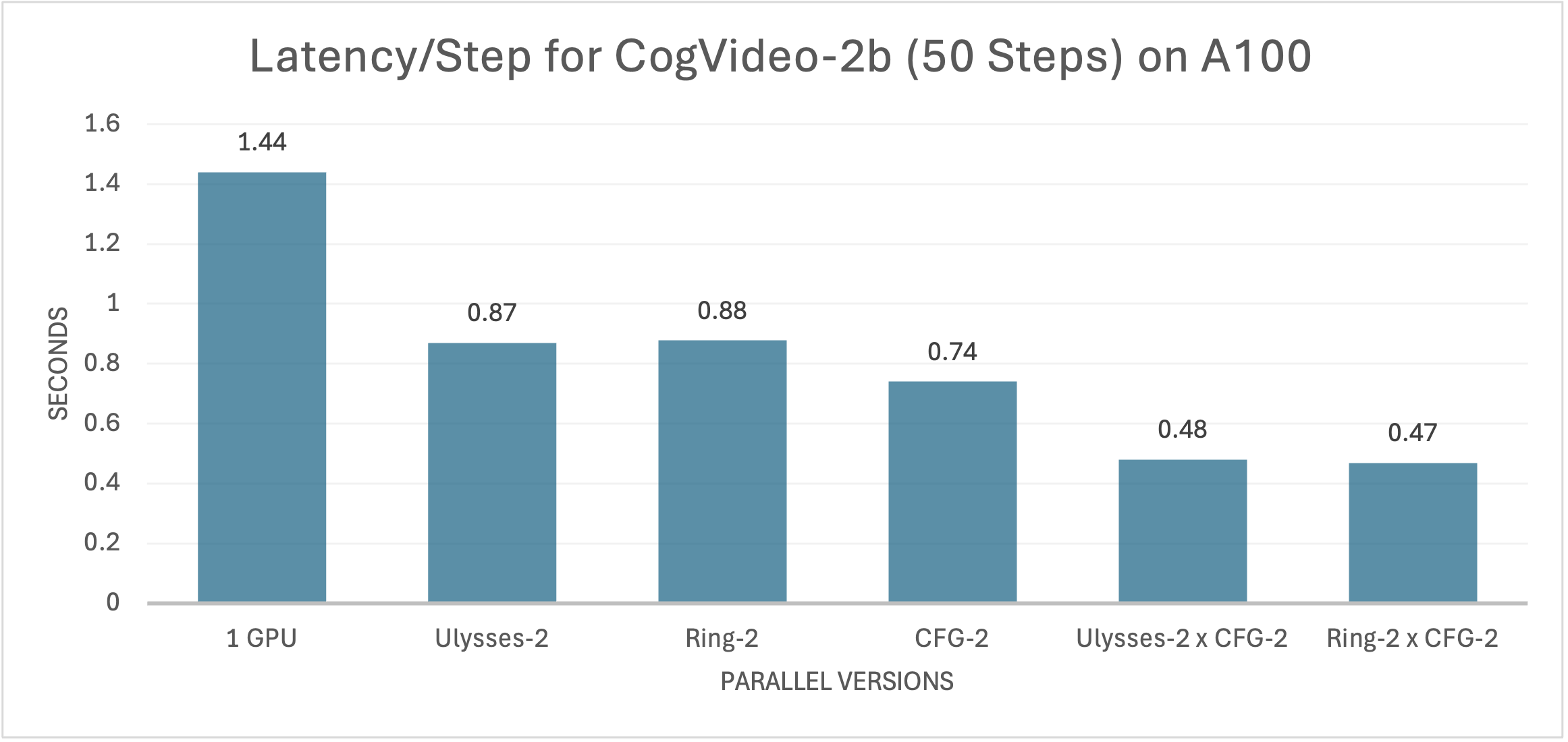
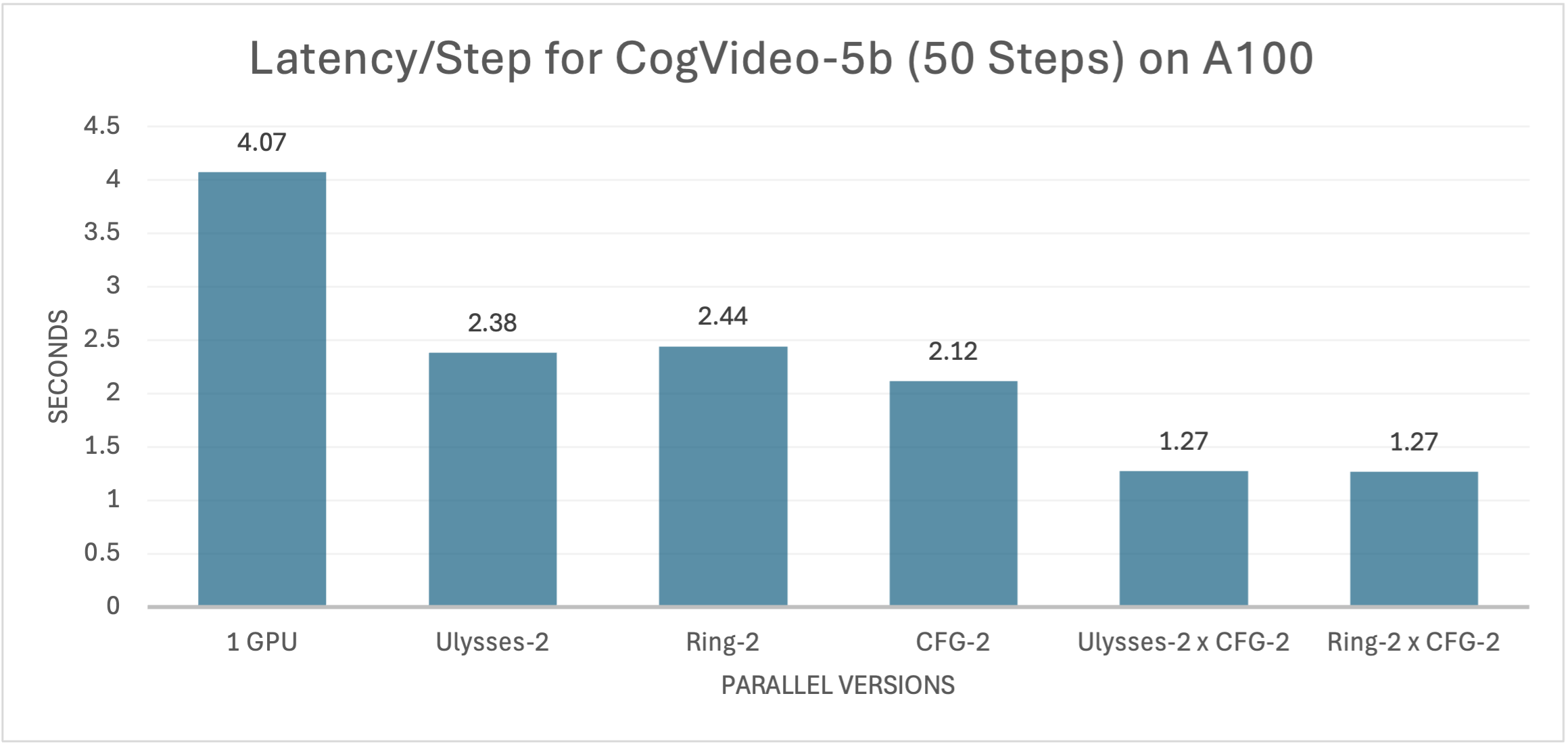
On systems equipped with A100 GPUs, xDiT demonstrates similar acceleration effects on CogVideoX-2b and CogVideoX-5b, as shown in the two figures below.
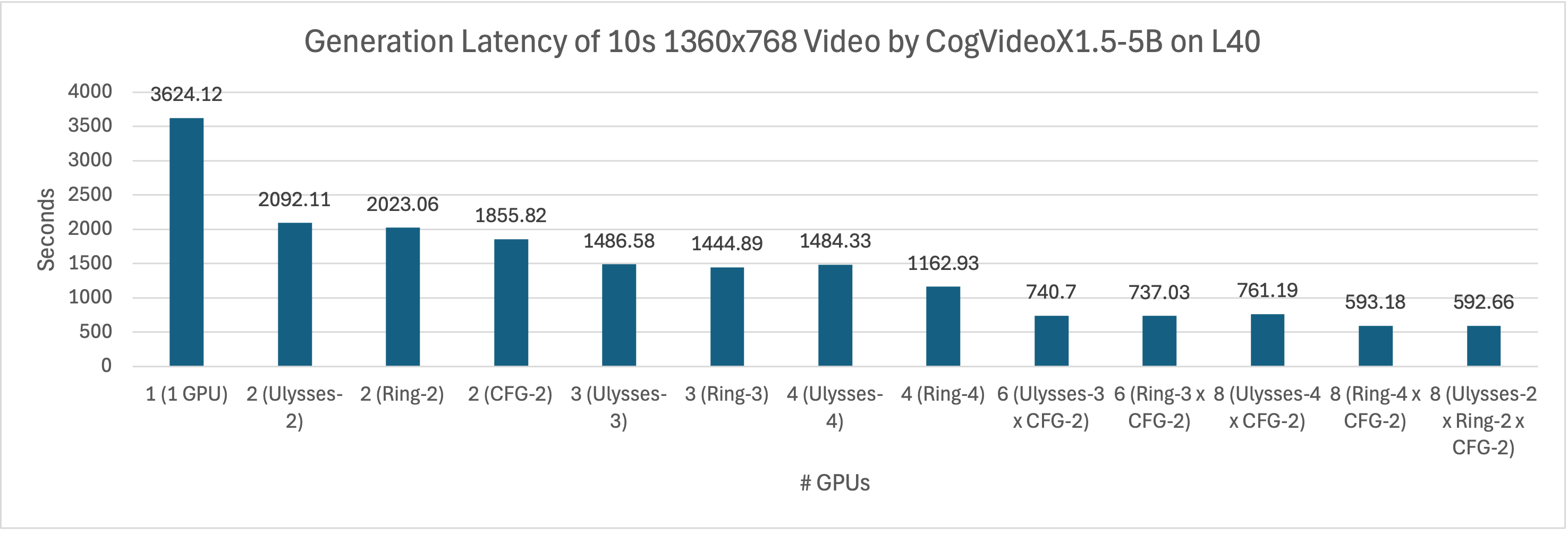
Similarly, we used CogVideoX1.5-5B to generate 161 frames of 1360x768 resolution video on a system equipped with an L40 (PCIe) GPU. We compared the inference latency of the single-card inference implementation in the diffusers library and the parallel version of xDiT. difference.
As shown in the figure, regardless of Ulysses Attention, Ring Attention or CFG parallelism, xDiT's inference latency can be reduced. Among them, when two GPU cards are given, CFG parallel shows higher performance than Ulysses Attention and Ring Attention due to smaller communication volume. By combining sequence parallelism and CFG parallelism, we further improve the inference efficiency. As parallelism increases, inference latency continues to decrease. In an 8-card environment, xDiT can achieve the best performance when mixing Ulysses-2, Ring-2, and CFG-2. Compared with the single-card inference method, it can achieve 6.12 times acceleration, and it takes less than 10 minutes to generate a video.
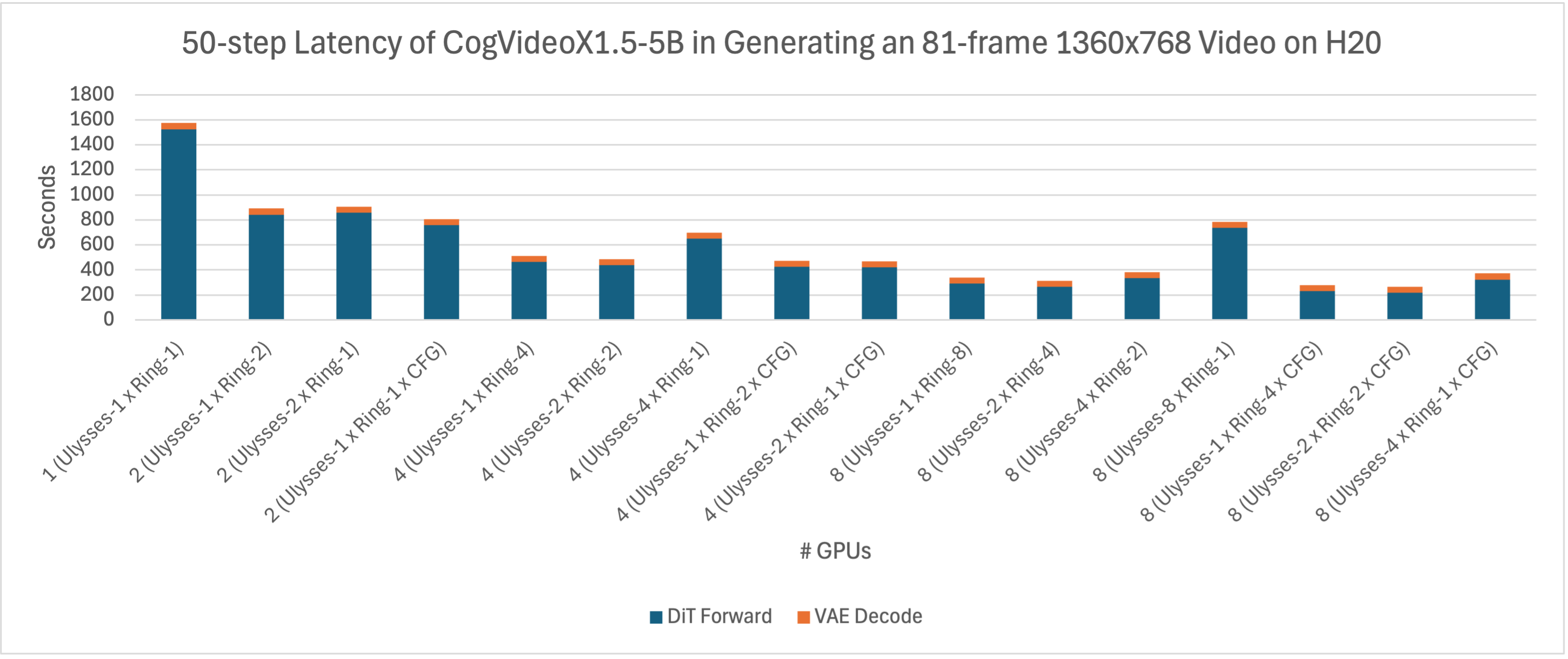
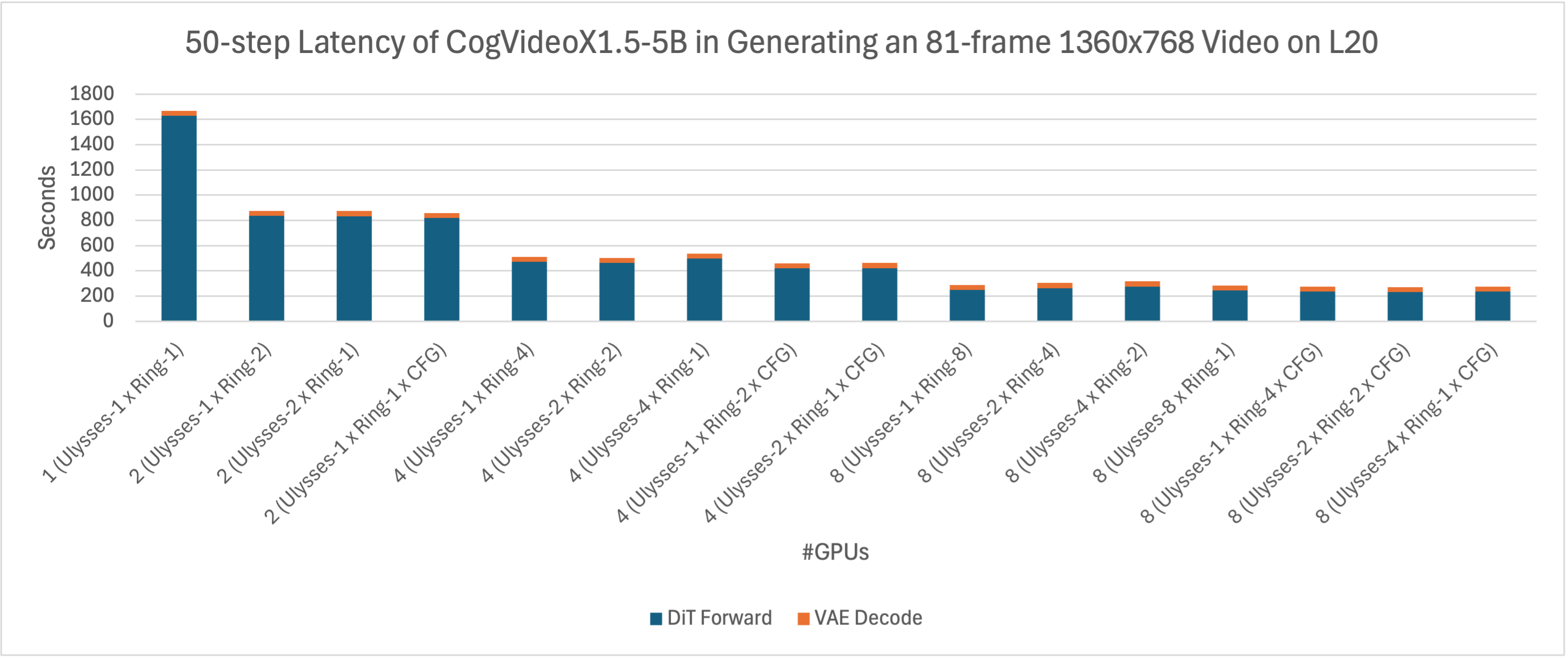
We further compared the acceleration effects of xDiT in generating a video of 81 frames at a resolution of 1360x768 on H20 and L20. As observed from the figure below, the inference latency of CogVideoX1.5-5B on these two devices is remarkably similar. Given the higher price of H20 compared to L20, L20 demonstrates a better cost-effectiveness.