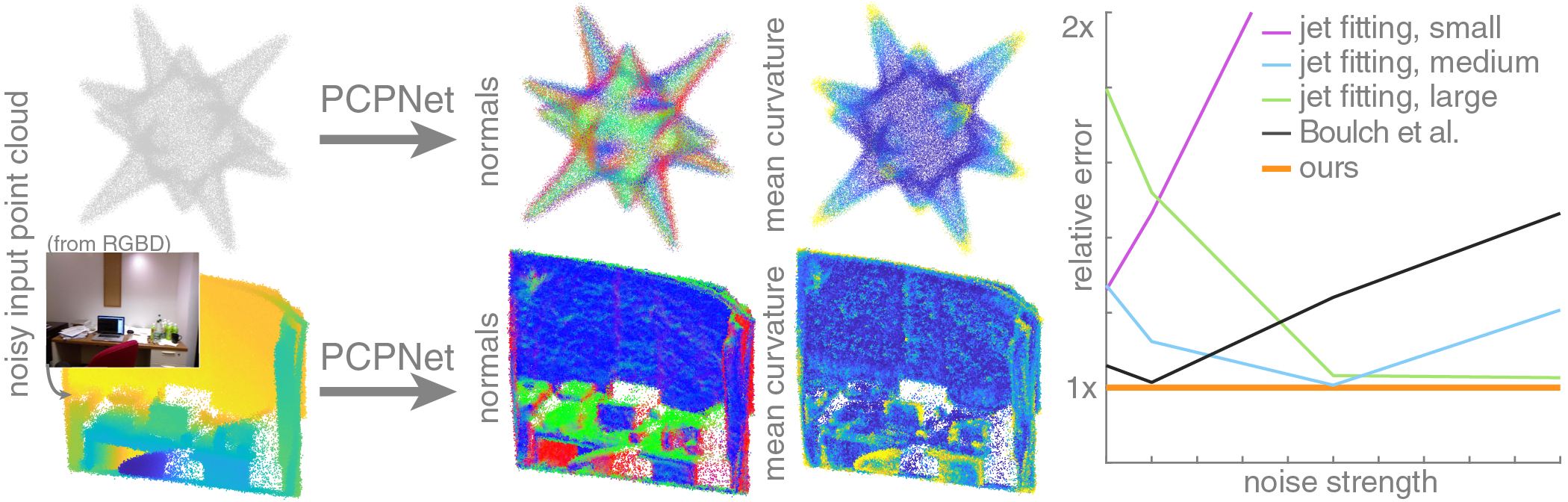
This is our implementation of PCPNet, a network that estimates local geometric properties such as normals and curvature from point clouds.
The architecture is similar to PointNet (with a few smaller modifications), but features are computed from local patches instead of of the entire point cloud, which makes estimated local properties more accurate.
This code was written by Paul Guerrero and Yanir Kleiman, based on the excellent PyTorch implementation of PointNet by Fei Xia.
This work was presented at Eurographics 2018.
Update 18/Oct/2018: The code has been updated to pytorch 0.4, and an option for choosing the GPU or using CPU only has been added. The old version that is compatible with pytorch 0.3 is still available in the branch pytorch_0.3.
Update 21/Jun/2018: The test dataset has been updated to include one shape that was missing to exactly reproduce the results in our paper. Thanks to Itzik Ben Shabat for pointing this out! Also note that the --sparse_patches option needs to be activated when running eval_pcpnet.py to exactly reproduce the results in our paper.
- Python 3.6
- PyTorch ≥ 0.4
- CUDA and CuDNN if training on the GPU
Install required python packages, if they are not already installed (tensorboardX is only required for training):
pip install numpy
pip install scipy
pip install tensorboardXClone this repository:
git clone https://github.com/paulguerrero/pcpnet.git
cd pcpnetDownload dataset and pre-trained models:
python pclouds/download_pclouds.py
python models/download_models.pyThe point cloud and its properties are stored in different files with the same name, but different extensions:
.xyz for point clouds, .normals for normals and .curv for curvature values.
These files have similar formats. Each line describes one point, containing (x, y, z) coordinates separated by spaces for points and normals and (max. curvature, min. curvature) values for curvatures.
A dataset is given by a text file containing the file name (without extension) of one point cloud per line. The file name is given relative to the location of the text file.
To estimate point cloud properties using default settings:
python eval_pcpnet.pyThis outputs unoriented normals using the single-scale normal estimation model described in the paper
for the test set used in the paper. To use alternative models and data sets, either edit the default arguments
defined in the first few lines of eval_pcpnet.py, or run eval_pcpnet.py with additional arguments:
python eval_pcpnet.py --indir "path/to/dataset" --dataset "dataset.txt" --models "/path/to/model/model_name"Where dataset.txt is a dataset as described above.
The model is given without the _model.pth suffix. For example the model file models/single_scale_normal_model.pth
would be specified as --models "models/single_scale_normal". In addition to the model file,
a file containing model hyperparameters and training parameters has to be available at the same location and with the same name,
but with suffix _params.pth. Both the model and the parameters file are available for all pre-trained models and
are generated when training with train_pcpnet.py.
To train PCPNet with the default settings:
python train_pcpnet.pyThis trains the single-scale normal estimation model described in the paper on the training set used in the paper. To train on a different dataset:
python train_pcpnet.py --indir "path/to/dataset" --trainset "dataset.txt"The dataset is given in the format described above. To change model settings or train a multi-scale model, see the description of the input arguments in the first few lines of train_pcpnet.py.
If you use our work, please cite our paper:
@article{GuerreroEtAl:PCPNet:EG:2018,
title = {{PCPNet}: Learning Local Shape Properties from Raw Point Clouds},
author = {Paul Guerrero and Yanir Kleiman and Maks Ovsjanikov and Niloy J. Mitra},
year = {2018},
journal = {Computer Graphics Forum},
volume = {37},
number = {2},
pages = {75-85},
doi = {10.1111/cgf.13343},
}